Home
Products
Chelidonic acid


| Product Name | Chelidonic acid |
| Price: | $62 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN06526 |
| CAS No.: | 99-32-1 |
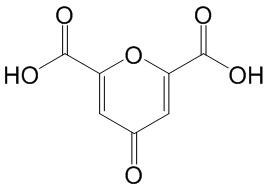
| Molecular Formula: | C7H4O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 184.10 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Miscellaneous |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Chelidonium majus |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | OC(=O)c1oc(cc(=O)c1)C(=O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Chelidonic acid is a component of Chelidonium majus L., used as a mild analgesic, an antimicrobial, an acentral nervous system sedative. Chelidonic acid also shows anti-inflammatory activity. Chelidonic acid has potential to inhibit IL-6 production by blocking NF-κB and caspase-1[1]. Chelidonic acid is a glutamate decarboxylase inhibitor, with a Ki of 1.2 μM[2]. |
| Target | NF-κB Caspase-1 Glutamate decarboxylase:1.2 μM (Ki) |
| In Vitro | Chelidonic acid dose-dependently decreases IL-6 production at 0.1-10 μM, inhibits expression of IL-6 mRNA at 1-10 μM[1]. Chelidonic acid (0.1-10 μM) decreases caspase-1 activation, nuclear NF-κB activation, and increases cytosol NF-κB activation[1]. Chelidonic acid is a glutamate decarboxylase inhibitor, with a Ki of 1.2 μM. Chelidonic acid does not promote formation of apoenzyme or react with free pyridoxal-P[2]. |
| In Vivo | Chelidonic acid (0.2, 2 mg/kg p.o.) attenuates allergic reaction induced by ovalbumin in mice[3]. |
| Density | 1.821 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 471.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 204.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 184.00100 |
| PSA | 104.81000 |
| LogP | 0.03620 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |