Home
Products
(-)-Epigallocatechin(EGC)
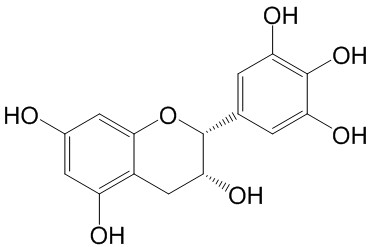


| Product Name | (-)-Epigallocatechin(EGC) |
| Price: | $43 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN05216 |
| CAS No.: | 970-74-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C15H14O7 |
| Molecular Weight: | 306.3 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Berchemia kulingensis Schneid. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1cc2O[C@H](c3cc(O)c(c(c3)O)O)[C@@H](Cc2c(c1)O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | (-)-Epigallocatechin is the most abundant flavonoid in green tea, can bind to unfolded native polypeptides and prevent conversion to amyloid fibrils.IC50 value:Target: in vitro: EGCG is a potent inhibitor of amyloidogenic cystatin I66Q amyloid fibril formation in vitro. Computational analysis suggests that EGCG prevents amyloidogenic cystatin fibril formation by stabilizing the molecule in its native-like state as opposed to redirecting aggregation to disordered, amorphous aggregates [1]. Combined curcumin and EGCG treatment reduced the cancer stem-like Cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44)-positive cell population. Western blot and immunoprecipitation analyses revealed that curcumin and EGCG specifically inhibited STAT3 phosphorylation and STAT3-NFkB interaction was retained [2]. EGCG exhibited a MIC and MBC of 5μg/mL and 20μg/mL respectively and effectively eradicated E. faecalis biofilms. EGCG induced the formation of hydroxyl radicals in E. faecalis. The addition of DIP protected E. faecalis against EGCG-mediated antibacterial effects. At sub-MIC, EGCG induced significant down-regulation of E. faecalis virulence genes [3]. |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 685.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 368.5±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 306.073944 |
| PSA | 130.61000 |
| LogP | -0.10 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |