Home
Products
Cinnamtannin A2
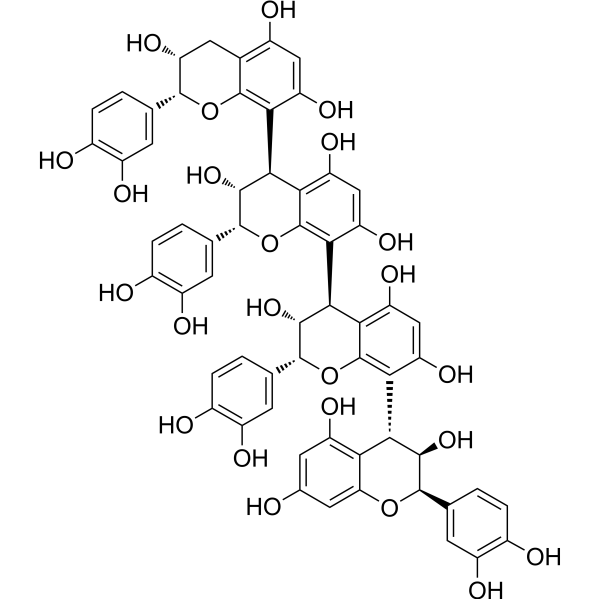


| Product Name | Cinnamtannin A2 |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN04318 |
| CAS No.: | 86631-38-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C60H50O24 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1155.1 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The seeds of Vitis vinifera L. |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
| SMILES: |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Cinnamtannin A2, a tetrameric procyanidin, can increases GLP-1 and insulin secretion in mice. Cinnamtannin A2 could upregulate the expression of corticotrophin releasing hormone. Cinnamtannin A2 exhibits antioxidant, anti-diabetic and nephroprotective effect[1][2]. |
| In Vitro | Cinnamtannin A2 (0.125-2.0 μg/mL) inhibits LDL oxidation induced by copper ions or MeO-AMVN[3]. |
| In Vivo | Cinnamtannin A2 (10 mg/kg; i.p. for 30 days) ameliorates the level of KIM1 and NAGL in 5/6 nephractomized rats by regulating Nrf2- Keap1 pathway[2]. Cinnamtannin A2 (10 μg/kg; p.o.) increases the secretion of insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in plasma of mice[1]. Cinnamtannin A2 (10 μg/kg; p.o.) significantly promotes phosphorylation of both IRB and IRS-1 in mice[1]. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250-300 g) were induced chronic renal failure (CRF) by removing the kidneys[2] Dosage: 10 mg/kg Administration: I.p. for 30 days Result: Ameliorated the altered level of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and cytokines in the serum and microalbuminurea. Reduced the oxidative stress level. Attenuated the altered expression of proteins involved in Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in the kidney tissue. Reduced the tubular injury score in the kidney tissue. |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Exact Mass | 1154.269165 |
| LogP | -0.07 |