Home
Products
Vinblastine


| Product Name | Vinblastine |
| Price: | $77 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN01389 |
| CAS No.: | 865-21-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C46H58N4O9 |
| Molecular Weight: | 810.96 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Catharanthus roseus (L.)G. Don |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
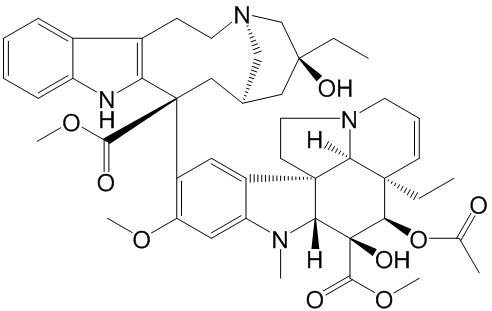
| SMILES: | COc1cc2N(C)[C@@H]3[C@@]4(c2cc1[C@]1(C[C@@H]2CN(CCc5c1[nH]c1c5cccc1)C[C@](C2)(O)CC)C(=O)OC)CCN1[C@H]4[C@@]([C@H]([C@]3(O)C(=O)OC)OC(=O)C)(CC)C=CC1 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Vinblastine is a cytotoxic alkaloid used against various cancer types. Vinblastine inhibits the formation of microtubule and suppresses nAChR with an IC50 of 8.9 μM. |
| Target | IC50: 8.9 μM(nAChR)[1] |
| In Vitro | Vinblastine does not depolymerize spindle microtubules, yet it powerfully blocks mitosis (for example, IC50 0.8 nM in HeLa cells) and cells die by apoptosis[2]. In NB4 cells, vinblastine produces alteration of p53 and DNA fragmentation. Vinblastine treatment has an antiproliferative effect via the induction of apoptosis producing Bax/Bcl-2 imbalance. Vinblastine treatment suppresses NFκB expression and depresses NFκB-DNA binding activity while maintaining JNK activation that subsequently results in apoptotic response through caspase-dependent pathway[3]. Vinblastine is found to trigger apoptosis as evidenced by the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, the release of both cytochrome c and apoptosis inducing factor, activation of caspase-9 and 3, and cleavage of Poly (ADP-ribose)-Polymerase[4]. |
| In Vivo | Vinblastine is a widely used anticancer drug with undesired side effects. Its conjugation with carrier molecules could be an efficient strategy to reduce these side effects[5]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Exact Mass | 810.420349 |
| PSA | 154.10000 |
| LogP | 4.18 |
| Storage condition | -20C |