Home
Products
Gnetol


| Product Name | Gnetol |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN03873 |
| CAS No.: | 86361-55-9 |
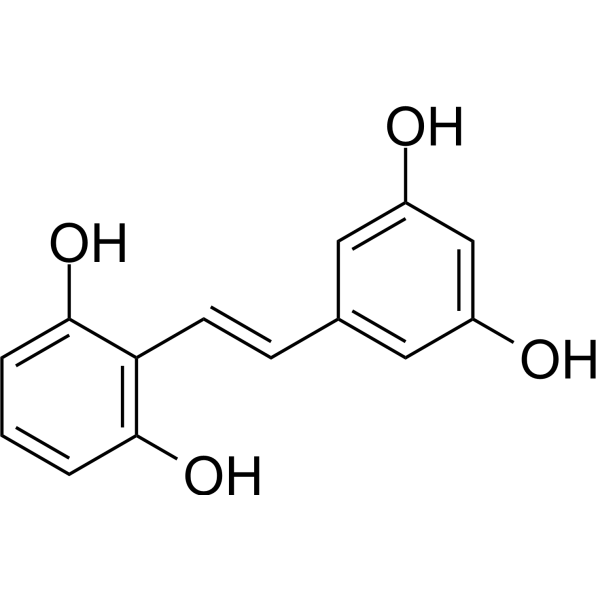
| Molecular Formula: | C14H12O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 244.2 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Phenols |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Gnetum cleistostachynm |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1cc(/C=C/c2c(O)cccc2O)cc(c1)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Gnetol is a phenolic compound isolated from the root of Gnetum ula Brongn. Gnetol potently inhibits COX-1 (IC50 of 0.78 μM) and HDAC. Gnetol is a potent tyrosinase inhibitor with an IC50 of 4.5 μM for murine tyrosinase and suppresses melanin biosynthesis. Gnetol has antioxidant, antiproliferative, anticancer and hepatoprotective activity. Gnetol also possesses concentration-dependent α-Amylase, α-glucosidase, and adipogenesis activities[1][2][3]. |
| Target | COX-1:0.78 μM (IC50) Tyrosinase:4.5 μM (IC50) HDAC |
| In Vitro | The antiproliferative activities of Gnetol are tested in HCT-116, Hep-G2, MDA-MB-231, and PC-3 cell lines by measuring cell viability after treatment with 4.1 μM, 40.9 μM, 204.7 μM, 409.4 μM, and 1023.6 μM. Gnetol shows concentration-dependent reductions in cell viability in cancer cell lines with greatest activity in colorectal cancer[1]. Gnetol at 200 µg/mL significantly offers the highest protection of 54.3% against the toxicant. A lower dose of Gnetol (50 µg/mL) also shields the cell line from the toxic effects of CCl4[3]. The ligand molecule TGF-β and PPARα protein show that Gnetol has the binding affinity of 7.0 and 8.4, respectively[3]. |
| In Vivo | Male Sprague-Dawley rats were cannulated and dosed either intravenously with Gnetol (10 μg/kg) or orally (100 mg/kg). After oral and intravenous administration, Gnetol is detected in both serum and urine as the parent compound and as a glucuronidated metabolite. The bioavailability of Gnetol is determined to be 6%. Gnetol is rapidly glucuronidated and is excreted in urine and via nonrenal routes[1]. Pretreatment of Male NIH Swiss mice (20-35 g) with Gnetol (50mg/kg, SC) is able to increase the latency period to response in analgesia models[1]. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 540.8±30.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 269.7±19.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 244.073563 |
| PSA | 80.92000 |
| LogP | 3.73 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |