Home
Products
Rotenone
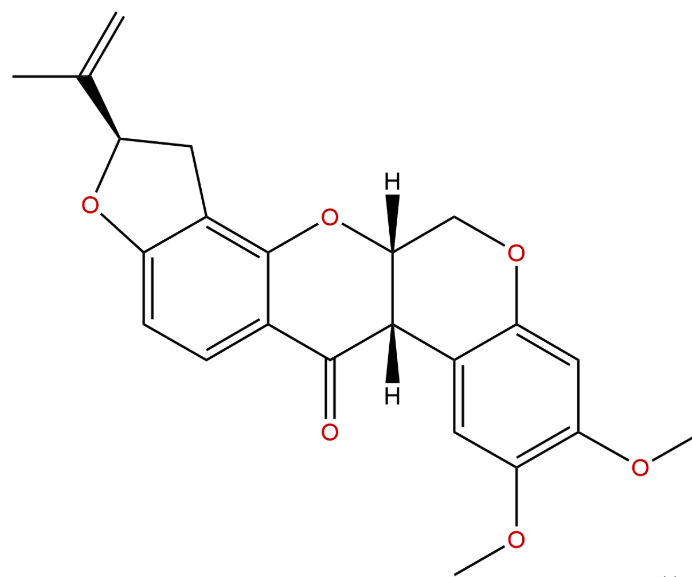


| Product Name | Rotenone |
| Price: | $12 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN05333 |
| CAS No.: | 83-79-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C23H22O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 394.42 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Derris trifoliata Lour. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COc1cc2c(cc1OC)OCC1C2C(=O)c2c(O1)c1CC(Oc1cc2)C(=C)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Rotenone is an mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I inhibitor. |
| In Vitro | Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), Toll-like receptor, Wnt, and Ras signaling pathways are intensively involved in the effect of rotenone on the ENS[2]. Rotenone-induced cell death is reduced by treatment as measured by decline in the levels of pro-apoptotic proteins. Moreover, treatment significantly augments the levels of anti-apoptotic Bcl2 and blocks the release of cytochrome c, thereby alleviating the rotenone-induced dopaminergic neuronal loss, as evidenced by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunostaining in the striatum[3]. |
| In Vivo | Rotenone causes a significant increase in the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters; glutamate and aspartate together with a significant decrease in the inhibitory amino acids, GABA, glycine and taurine are observed in the cerebellum of rat model of PD[1]. Rotenone (1.5, 2, or 2.5 mg/kg) causes a dose-dependent increase in α-synuclein in the substantia nigra. Furthermore, at 2 and 2.5 mg/kg, rotenone causes a significant decrease in the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the substantia nigra, and dopamine in the striatum in rats[4]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 559.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 244.6±30.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 394.141632 |
| PSA | 63.22000 |
| LogP | 4.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |