Home
Products
Visnagin


| Product Name | Visnagin |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN05245 |
| CAS No.: | 82-57-5 |
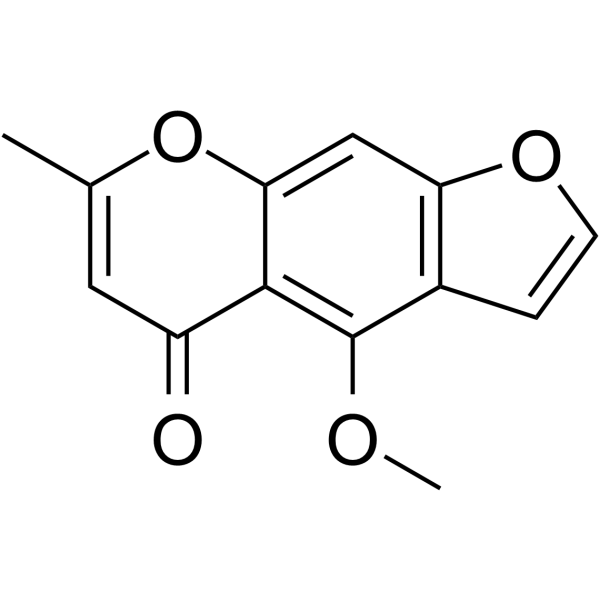
| Molecular Formula: | C13H10O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 230.2 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Yellow powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Ammi visnaga. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COc1c2c(=O)cc(oc2cc2c1cco2)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Visnagin, an antioxidant furanocoumarin derivative, possess anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Visnagin has substantial potential to prevent Cerulein induced acute pancreatitis (AP). Visnagin possess promising vasodilator effects in vascular smooth muscles[1][2]. |
| In Vitro | Visnagin (10 µM; for 4, 8, 16, 24 h) induces CYP1A1 transcription in HepG2 cells[1]. Visnagin (10 µM; for 16 h) elevates CYP1B1 gene expression in an aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-dependent manner, whereas MNF (3’-methoxy-4’-nitroflavone; 20 µM; pre-treated for 1 h) successfully counteracted this induction. Visnagin also enhances PAI-2 transcription in an AHR-dependent manner[1]. |
| In Vivo | Visnagin (10, 30, 60 mg/kg; ip; for 7 days) is effective in reducing plasma amylase and lipase levels and reduces Cerulein (50 μg/kg, six, hourly i.p. injections) induced oxidative stress in male Swiss albino mice (age: 6-8 weeks, weighing 20-25 g)[1]. Visnagin dose dependently decreases the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and IL-17. It attenuates the levels of nuclear p65-NFκB. Visnagin improves the antioxidant defence by improving Nrf2 expression and halts pancreatic inflammation by suppressing NFκB and nitrotyrosine expression in the acinar cells[1]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 378.2±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 182.5±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 230.057907 |
| PSA | 52.58000 |
| LogP | 2.26 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C |