Home
Products
Roxadustat (FG-4592)


| Product Name | Roxadustat (FG-4592) |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00357 |
| CAS No.: | 808118-40-3 |
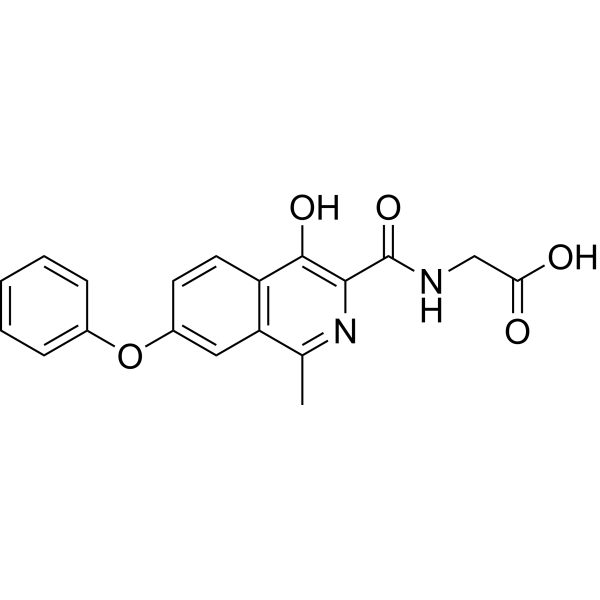
| Molecular Formula: | C19H16N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 352.34 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | OC(=O)CNC(=O)c1nc(C)c2c(c1O)ccc(c2)Oc1ccccc1 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Roxadustat (FG-4592) is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor developed for the treatment of anemia. |
| In Vitro | Roxadustat significantly increases accumulation of HIF-1α and BNIP3, resultes in reduced TUNEL-positive photoreceptors 3 days after RD and an increased thickness of the outer nuclear layer 7 days after RD in the TUNEL-positive cells[1]. Roxadustat increases differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) under both hypoxia and normoxia[2]. |
| In Vivo | Roxadustat (25 mg/kg) enhances mitophagy and attenuates retinal histopathologic damage in the photoreceptor layer after RD in an RD animal model[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The left eye of each rat is retro-orbitally injected with 25 mg/kg FG-4592 every 2 days, and an equal volume of 20% DMSO diluted with 0.9% NaCl is administrated with retro-orbital injection and served as the control. The retinae (attached, 1 day, 3 days, 5 days, and 7 days after RD) are homogenized and lysed with buffer containing 50 mM hydroxymethyl(Tris)-aminomethane(HCl), 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, and a protease inhibitor tablet. Samples are run on 8% to 12% 2-hydroxyethyl (Bis)-hydroxymethyl (Tris) gel electrophoresis and transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (0.2-mm pores). After blocking with 3% nonfat dried milk, the membranes are incubated overnight with primary antibody HIF-1α, LC3, BNIP3, autophagy-related gene 5 (Atg5), and β-actin. The blotted membranes are then incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature with a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled secondary antibody. Immunoreactive bands are visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) and detected with an Amersham Imager 600. A minimum of three rats are used for each condition. |
| Animal Admin | The rats are anesthetized with 1% sodium pentobarbital, and the pupils are dilated with 0.5% tropicamide and 0.5% phenylephrine hydrochloride eye drops. In each rat, the sclera is punctured approximately 1.5 mm posterior to the limbus with a 30-gauge needle with special caution taken to avoid damaging the lens. The needle is slowly advanced into the vitreous cavity through the sclerotomy and then to the subretinal space by producing a small hole in the peripheral retina. Sodium hyaluronate (10 mg/mL) is slowly injected until almost two-thirds of the neurosensory retina detached from the underlying RPE. RD is confirmed for each rat by a surgical microscope. The blebs of RD are created and remained essentially stable for 7 days. All of the procedure steps are performed on the left eyes of the control group, except for the introduction of the subretinal injector and injection of the sodium hyaluronate. A total of 102 rats are used, and all animal experiments contained at least three rats per group. Roxadustat is dissolved in 20% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride (NaCl). The left eye of each rat is retro-orbitally injected with 25 mg/kg Roxadustat every 2 days, and an equal volume of 20% DMSO diluted with 0.9% NaCl is administrated with retro-orbital injection and served as the control. All of the detection time points are selected at 4 to 6 hours after retro-orbital injection. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 684.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 367.6±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 352.105927 |
| PSA | 108.75000 |
| LogP | 3.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |