Home
Products
Soybean phospholipid
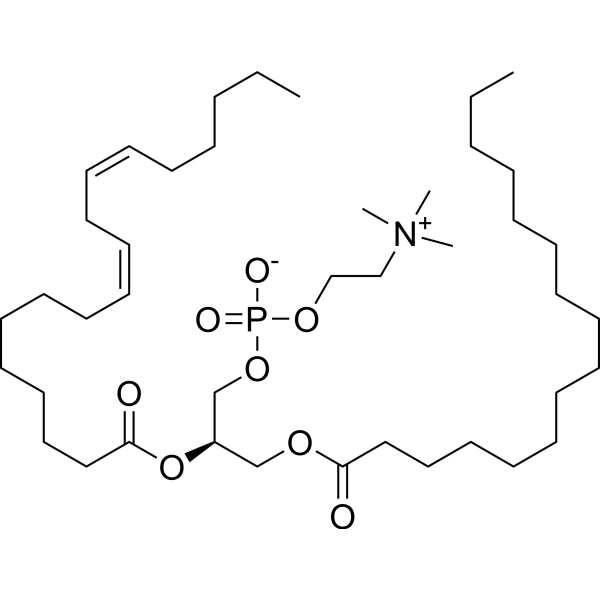


| Product Name | Soybean phospholipid |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN06536 |
| CAS No.: | 8002-43-5 |
| Molecular Formula: | C42H80NO8P |
| Molecular Weight: | 758.1 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Miscellaneous |
| Physical Desc.: | Solid |
| Source: | The seeds of Glycine max. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | CCCCCCCC/C=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(OC(=O)CCCCCCC/C=CCCCCCCCC)COP(=O)(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)[O-] |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Lecithin is regarded as a safe, conventional phospholipid source. Phospholipids are reported to alter the fatty acid composition and microstructure of the membranes in animal cells. |
| In Vitro | After culturing in MRS broth with 0.2 to 1.0% soy Lecithin, the survival rate of harvested cells increases significantly (P<0.05) in the 0.3% bile challenge compare with the no added soy Lecithin group. The cells incubated with 0.6% soy Lecithin are able to grow in an MRS broth with a higher bile salt content. The cell surface hydrophobicity is enhanced and the membrane integrity in the bile challenge increases after culturing with soy Lecithin. A shift in the fatty acid composition is also observed, illustrating the cell membrane changes in the soy Lecithin culture[1]. |
| Cell Assay | MRS broths are supplemented with soy Lecithin concentrations of 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0%. Each broth is inoculated with a tested strain culture (2%, v/v) and anaerobically incubated at 37°C for 20 h. After incubation, the bacterium cells are harvested by centrifugation at 8000 g for 10 min at 4°C and washed twice in PBS (pH 6.5) plus ethanol (5%, v/v). Strain bile resistance is assessed. The numbers of viable cells are counted by the pouring plate method, and each batch is tested three times[1]. |
| Density | 1.0305 g/cm3 (20ºC) |
| Flash Point | 57 °C |
| Exact Mass | 757.562134 |
| PSA | 121.00000 |
| LogP | 10.90 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |