Home
Products
Acetylaconitine
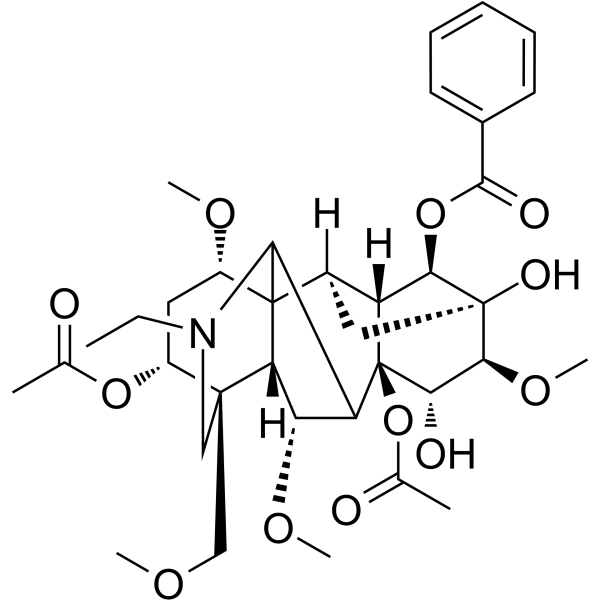


| Product Name | Acetylaconitine |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN01372 |
| CAS No.: | 77181-26-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C36H49NO12 |
| Molecular Weight: | 687.78 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Aconitum kusnezoffii Reichb. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COC[C@@]12CN(CC)C3C4([C@@H]2[C@@H](OC)C3[C@@]2([C@@H]3[C@H]4C[C@@]([C@@H]3OC(=O)c3ccccc3)([C@H]([C@@H]2O)OC)O)OC(=O)C)[C@H](C[C@H]1OC(=O)C)OC |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Flaconitine is isolated from the ammonium hydroxide wetted root of A.szechenyianum Gay. Flaconitine is considered to be a NF-κB inhibitor. |
| Target | NF-κB |
| In Vitro | Flaconitine has been demonstrated to suppress TNF-α induced NF-κB activation and is considered as a diester-diterpenoid-type NF-κB inhibitor[1] Flaconitine (3-Acetylaconitine) is evaluated for its cytotoxic activity against human leukemic P388 cells using the SRB (Sulforhodamine B) method, with Etoposide as the positive control. The cell growth inhibitory potency of Flaconitine is expressed as IC50 (μM) Value. Flaconitine exhibits moderately cytotoxic activity with an IC50 of 18.6 μM[2]. |
| Cell Assay | The assay is performed following a standard published procedure using microtiter plate format and sulforhodamine B standing at the end point. The leukemic cells (P388) are exposed to Flaconitine (3-Acetylaconitine) for three days. Cells are grown and maintained in an incubator set at 37°C, 5% CO2 and 95% humidity. RPMI-1640 media supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) and 0.5% trypsin are used to culture P388 cells[2]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 715.9±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 386.8±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 687.325500 |
| PSA | 159.52000 |
| LogP | 0.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |