Home
Products
Methylophiopogonanone A


| Product Name | Methylophiopogonanone A |
| Price: | $263 / 10mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN05332 |
| CAS No.: | 74805-92-8 |
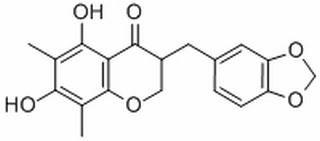
| Molecular Formula: | C19H18O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 342.34 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Ophiopogon japonicus |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | O=C1[C@@H](COc2c1c(O)c(C)c(c2C)O)Cc1ccc2c(c1)OCO2 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Methylophiopogonanone A, a major homoisoflavonoid in Ophiopogon japonicas, has both anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties[1]. |
| In Vitro | Methylophiopogonanone A (MO-A; 10 μmol/L) significantly decreases apoptosis and cleaved caspase-3 expression, elevated the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and restored NO production. Pretreatment with Methylophiopogonanone A (MO-A) markedly increases the activation of PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in H9C2 cells subjected to H/R, and the protective effects of MO-A are abolished in the presence of the PI3K inhibitor wortmannin (100 nmol/L)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Methylophiopogonanone A (MO-A;10 mg/kg/d, po) for 2 weeks) protects cardiac function following myocardial I/R injury[1]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 580.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 212.9±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 342.110352 |
| PSA | 85.22000 |
| LogP | 5.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |