Home
Products
Melatonin


| Product Name | Melatonin |
| Price: | $18 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN01987 |
| CAS No.: | 73-31-4 |
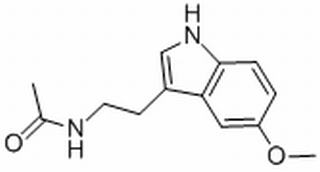
| Molecular Formula: | C13H16N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 232.28 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COc1ccc2c(c1)c(CCNC(=O)C)c[nH]2 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Melatonin is a hormone made by the pineal gland that can activates melatonin receptor. Melatonin plays a role in sleep and possesses important antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. |
| Target | Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | Melatonin increases the levels of activated PTEN, RSK-1, mTOR and AMPKα kinases, mildly inhibits ERK-1/2 phosphorylation and Bad phosphorylation, significantly inhibits phosphorylations of S6 Ribosomal Protein, 4E-BP1, GSK-3α and GSK-3β, and slightly increases PRAS40 phosphorylation in animals[1]. Melatonin ameliorates the neurotoxiciy and astrocyte activation induced by Aβ1-42 in the cerebral cortex. Melatonin also blocks the reduction in Reelin and Dab1 expression induced by Aβ1-42[2]. Melatonin treatment and lack of NLRP3-/- share similar inhibition of NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathway in mice. Melatonin treatment and lack of NLRP3-/- share some patterns of clock genes expression, and improve cardiomyocytes morphology in mice[3]. |
| Animal Admin | A total of two sets of adult male C57BL/6j mice weighing 21-26 g are randomly assigned to one of four groups and treated with intraperitoneal (i.p.) delivery of (i) vehicle (50 μL isotonic saline/5% ethanol), (ii) melatonin (4 mg/kg, dissolved in 0.9% isotonic saline/5% ethanol), (iii) Wortmannin, and (iv) melatonin/Wortmannin immediately after reperfusion. In the first set, mice are exposed to 30 min of focal cerebral ischemia (FCI) and 72 h reperfusion for the evaluation of disseminate ischemic injury in the striatum, and signaling pathway analysis (n=7 per group). The second group of mice is exposed to 90 min of FCI and 24 h reperfusion for the analysis of infarct development, brain swelling and IgG extravasation (n=7 per group). |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 459.8±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 231.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 232.121185 |
| PSA | 54.12000 |
| LogP | 1.94 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | -15°C |