Home
Products
Epiberberine
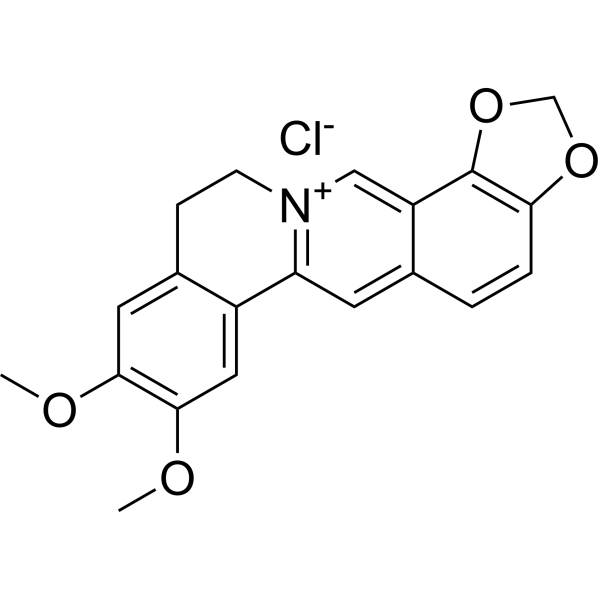


| Product Name | Epiberberine |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN02035 |
| CAS No.: | 6873-09-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C20H18NO4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 336.36 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The tubers of Corydalis decumbens (Thunb.) Pers. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COc1cc2c(cc1OC)CC[n+]1c2cc2ccc3c(c2c1)OCO3 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Epiberberine is an alkaloid isolated from Coptis chinensis, acts as a potent AChE and BChE inhibitor, and a non-competitive BACE1 inhibitor, with IC50s of 1.07, 6.03 and 8.55 μM, respectively. Epiberberine has antioxidant activity, with peroxynitrite ONOO- scavenging effect (IC50, 16.83 μM), and may protect against Alzheimer disease[1]. Epiberberine inhibits the early stage of differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, downregulates the Raf/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 and AMPKα/Akt pathways[2]. Epiberberine has the potential effect in the research of diabetic disease[3]. |
| Target | IC50: 1.07 μM (AChE), 6.03 μM (BChE), 8.55 μM (BACE1)[2] |
| In Vitro | Epiberberine (0, 12.5, 25, or 50 μM) dose-dependently inhibits cellular triglyceride accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, with an IC50 of 52.8 μM[2]. Epiberberine (12.5-50 μM) suppresses the Raf/MEK1/ERK1/2 and AMPKα/Akt pathways in the early stage of 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation[2]. Epiberberine (0.2, 1, 5 μg/mL) inhibits glucose uptake in HepG2 cells in a concentration-dependent manner[3]. |
| In Vivo | Epiberberine (225 mg/kg, p.o. daily for 40 days) reduces body weight, food consumption, water intake, and urinary output of KK-Ay mice[3]. |
| PSA | 40.80000 |
| LogP | -0.99 |
| Storage condition | 2-8C |