Home
Products
Dehydroevodiamine


| Product Name | Dehydroevodiamine |
| Price: | $54 / 10mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN01027 |
| CAS No.: | 67909-49-3 |
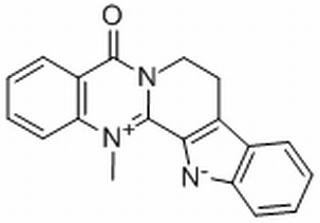
| Molecular Formula: | C19H15N3O |
| Molecular Weight: | 301.4 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Yellow powder |
| Source: | The fruits of Evodia rutaecarpa. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | C[n+]1c2ccccc2c(=O)n2c1c1[n-]c3c(c1CC2)cccc3 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Dehydroevodiamine is a major bioactive quinazoline alkaloid isolated from Evodiae Fructus, has an antiarrhythmic effect in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes[1]. Dehydroevodiamine inhibits LPS-induced iNOS, COX-2, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) expression in murine macrophage cells[2]. |
| Target | iNOS; COX-2; PGE2; NF-κB[2] |
| In Vitro | Dehydroevodiamine (0-50 μM; 2 hours) inhibits iNOS and COX-2 expression and prevents degradation of IκB-α in LPS induced RAW 264.7 macrophages[2]. Dehydroevodiamine (0-50 μM; 2 hours) inhibits a LPS-induced increase in the iNOS and COX-2 mRNA expression[2]. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: RAW 264.7 macrophage cells Concentration: 10 μM, 30 μM, 50 μM Incubation Time: pretreated 2 hours Result: Reduced iNOS and COX-2 expression and increased IκB-α expression. RT-PCR[2] Cell Line: RAW 264.7 macrophage cells Concentration: 10 μM, 30 μM, 50 μM Incubation Time: pretreated 2 hours Result: Reduced iNOS and COX-2 mRNA expression. |
| Exact Mass | 301.121521 |
| PSA | 38.77000 |
| LogP | 2.15950 |
| Storage condition | 2-8C |