Home
Products
Gastrodin
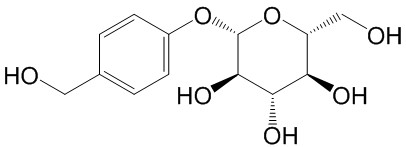


| Product Name | Gastrodin |
| Price: | $12 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN04112 |
| CAS No.: | 62499-27-8 |
| Molecular Formula: | C13H18O7 |
| Molecular Weight: | 286.28 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Phenols |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Gastrodia elata BL. |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
| SMILES: | OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](Oc2ccc(cc2)CO)[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1O)O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Gastrodin, a main constituent of a Chinese herbal medicine Tianma, has been known to display anti-inflammatory effects. Gastrodin, has long been used for treating dizziness, epilepsy, stroke and dementia. |
| In Vitro | Gastrodin treatment reduces the mRNA expression levels of TNF-α and iNOS in the retinas of acute ocular hypertension[1]. |
| In Vivo | Intraperitoneal injection with Gastrodin 10 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg once daily for 15 d significantly inhibits the loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) because of acute ocular hypertension (AOH) damage. 2 wk after AOH, the number of Iba1 positive retinal microglia obviously reduces to 231.3±54.3 cells/mm2 and 201.9±43.1 cells/mm2 in the rats intraperitoneally injected with Gastrodin at 10 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg, respectively[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Retinas are collected at day 14 postoperatively, following treatment with normal saline (NS) or various doses of Gastrodin. The mRNA expression levels of TNF-α and iNOS are determined by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Adult female SD rats (age, 8 wk; weight, 200 to 250 g) are used. The rats are divided into 4 groups: 1) control group; 2) normal saline (NS) group who are exposed to acute ocular hypertension (AOH) and receive intraperitoneal injection of 0.9% NS; 3) G10 group who are exposed to AOH and receive intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg Gastrodin; 4) G50 group who are exposed to AOH and receive intraperitoneal injection of 50 mg/kg Gastrodin. The loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and the number of Iba1-positive retina microglia are determined at 2 wk after rapid ocular hypertension[1]. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 563.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 294.4±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 286.105255 |
| PSA | 119.61000 |
| LogP | -1.85 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |