Home
Products
Quercetin Dihydrate


| Product Name | Quercetin Dihydrate |
| Price: | $23 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN04830 |
| CAS No.: | 6151-25-3 |
| Molecular Formula: | C15H14O9 |
| Molecular Weight: | 338.3 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The flower buds of Sophora flavescens Ait. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
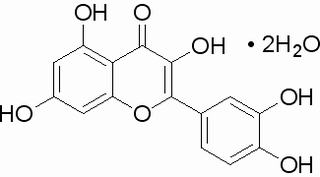
| SMILES: | Oc1cc(O)c2c(c1)oc(c(c2=O)O)c1ccc(c(c1)O)O.O.O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Quercetin (dihydrate), a natural flavonoid, is a stimulator of recombinant SIRT1 and a PI3K inhibitor with IC50s of 2.4 μM, 3.0 μM and 5.4 μM for PI3K γ, PI3K δ and PI3K β, respectively[1]. |
| Target | PI3Kγ:2.4 μM (IC50) PI3Kβ:5.4 μM (IC50) PI3Kδ:3.0 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Quercetin (dihydrate) is a type of plant-based chemical, or phytochemical, used as an ingredient in supplements, beverages or foods. In several studies, it may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, and it is being investigated for a wide range of potential health benefits[1]. Quercetin (dihydrate) is a PI3K inhibitor with IC50s of 2.4-5.4 μM. Quercetin dihydrate (Sophoretin dihydrate) strongly abrogates PI3K and Src kinases, mildly inhibits Akt1/2, and slightly affected PKC, p38 and ERK1/2[1]. Quercetin (dihydrate) inhibits TNF-induced LDH% release, EC-dependent neutrophils adhesion to bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells (BPAEC), and BPAEC DNA synthesis and proliferation[2]. |
| Boiling Point | 642.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Exact Mass | 338.063782 |
| PSA | 149.82000 |
| LogP | 1.85940 |