Home
Products
Liquiritigenin
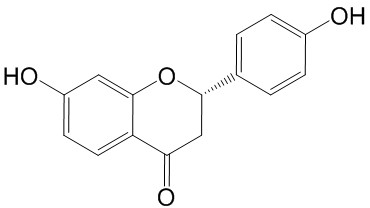


| Product Name | Liquiritigenin |
| Price: | $31 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN05543 |
| CAS No.: | 578-86-9 |
| Molecular Formula: | C15H12O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 256.25 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1ccc(cc1)[C@@H]1CC(=O)c2c(O1)cc(cc2)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Liquiritigenin, a flavanone isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, is a highly selective estrogen receptor β (ERβ) agonist with an EC50 of 36.5 nM for activation of the ERE tk-Luc. |
| Target | EC50: 36.5 nM (activation of the ERE tk-Luc)[1] |
| In Vitro | Liquiritigenin produces a dose-response activation of ERE tk-Luc in the U2OS cells transfected with ERβ, but not ERα. Liquiritigenin produces a dose-dependent activation and a time-dependent increase of the CECR6, NKG2E and NKD with ERβ but not with ERα. The ERβ-selectivity of liquiritigenin is due to the selective recruitment of the coactivator steroid receptor coactivator-2 to target genes. Liquiritigenin exhibits similar binding affinities for ERα and ERβ, and causes the recruitment of SRC-2 to target genes selectively in ERβ cells[1]. Pretreatment of MC3T3-E1 cells with liquiritigenin prevents the MG-induced cell death and production of protein adduct, intracellular reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial superoxide, cardiolipin peroxidation, and TNF-α in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | In a mouse xenograph model, liquiritigenin does not stimulate uterine size or tumorigenesis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells[1]. Treatment with liquiritigenin significantly reduces the concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in serum and hippocampus[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: MCF-7 (250,000) cells are grafted under the kidney capsule of nude mice. Five mice per group are treated with a continuous infusion using osmotic pumps containing vehicle, E2 (0.4 mg) or liquiritigenin (2 mg) that infused 2.5 μL/h for 1 month. After one month of treatment, the tumors and uteri are removed and analyzed[1]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 529.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 206.9±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 256.073547 |
| PSA | 66.76000 |
| LogP | 2.76 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |