Home
Products
Fraxin
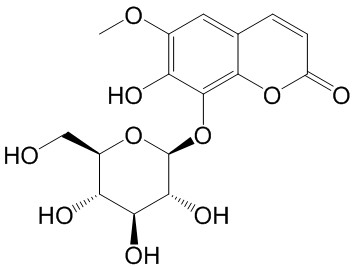


| Product Name | Fraxin |
| Price: | $46 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN06297 |
| CAS No.: | 524-30-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C16H18O10 |
| Molecular Weight: | 370.32 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Coumarins |
| Physical Desc.: | White powder |
| Source: | The barks of Fraxinus brngeana DC. |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
| SMILES: | OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](Oc2c(O)c(OC)cc3c2oc(=O)cc3)[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1O)O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Fraxin isolated from Acer tegmentosum, F. ornus or A. hippocastanum, is a glucoside of fraxetin and reported to exert potent anti-oxidative stress action[1], anti-inflammatory and antimetastatic properties. Fraxin shows its antioxidative effect through inhibition of cyclo AMP phosphodiesterase enzyme[2]. |
| Target | Cyclo AMP phosphodiesterase enzyme[2]. |
| In Vitro | Fraxin (100 μM) is non-cytotoxic on Hep G2 cells. Fraxin at non-cytotoxic concentrations significantly decreases the t-BHP-induced ROS generation in a dose-dependent manner[1]. Fraxin (0.5 mM) shows free radical scavenging effect at high concentration and cell protective effect against H2O2-mediated oxidative stress[2]. |
| In Vivo | Fraxin (50 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly blocks the CCl4-induced elevation of ALT and AST. Fraxin (10 and 50 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reduces the GSSG levels (1.7±0.3 and 1.5±0.2 nM/g liver, respectively) compared with the GSSG levels of the CCl4-treated group[1]. |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 722.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 267.1±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 370.089996 |
| PSA | 159.05000 |
| LogP | -1.93 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |