Home
Products
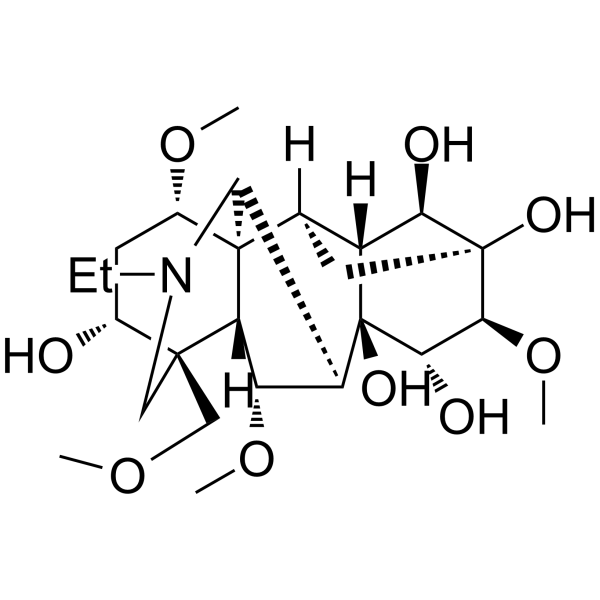
Aconine


| Product Name | Aconine |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN01381 |
| CAS No.: | 509-20-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C25H41NO9 |
| Molecular Weight: | 499.60 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Aconitum kusnezoffii Reichb. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COC[C@@]12CN(CC)C3C4([C@@H]2[C@@H](OC)C3[C@@]2([C@@H]3[C@H]4C[C@@]([C@@H]3O)([C@H]([C@@H]2O)OC)O)O)[C@H](C[C@H]1O)OC |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Aconine inhibits receptor activator of nuclear factor (NF)-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced NF-κB activation. |
| Target | NF-κB |
| In Vitro | Treatment with Aconine significantly inhibits the RANKL-induced transcriptional activity of NF-κB in a dose-dependent manner. Aconine inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and NFATc1 and the expression of the cell-cell fusion molecule DC-STAMP. Aconine (0.125, 0.25 μM) does not affect the viability of RAW264.7 cells, but dose-dependently inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorptive activity. Aconine dose-dependently inhibits the RANKL-induced activation of NF-κB and NFATc1 in RAW264.7 cells, and subsequently reduces the expression of osteoclast-specific genes (c-Src, β3-Integrin, cathepsin K and MMP-9) and the expression of dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP), which plays an important role in cell-cell fusion[1]. |
| Cell Assay | To evaluate the effect of Aconine on the viability of RAW264.7 cells, cytotoxicity assays are performed using the Cell Counting Kit-8. Briefly, the cells are seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 2×104, 3×103, 1.2×103, 1×103 or 1×103 cells/well in the presence or absence of Aconine (0.125-0.5 mM) for 8 h, 24 h, 48 h, 5 d or 7 d, respectively. After incubating the cells with CCK-8 solution for 2 h, optical density is measured at 450 nm using a GENios microplate reader. Cell viability is expressed as a percentage of the control[1]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 626.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 332.4±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 499.278137 |
| PSA | 141.31000 |
| LogP | -1.63 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.1 mmHg at 25°C |