Home
Products
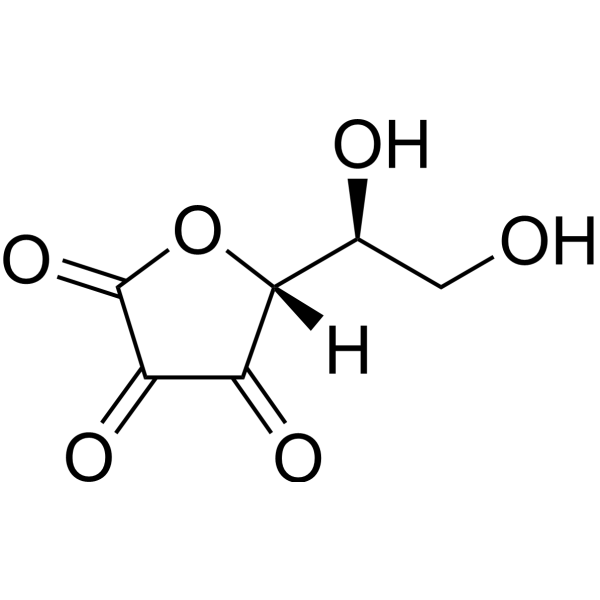
Dehydroascorbic acid


| Product Name | Dehydroascorbic acid |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN06435 |
| CAS No.: | 490-83-5 |
| Molecular Formula: | C6H6O6 |
| Molecular Weight: | 174.1 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Miscellaneous |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The fruit of Orange. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | OC[C@@H]([C@H]1OC(=O)C(=O)C1=O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Dehydroascorbic acid, a blood-brain barrier transportable form of vitamin C, mediates potent cerebroprotection in experimental stroke. |
| Target | Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Neuronal injury in ischemic stroke is partly mediated by cytotoxic reactive oxygen species. Although the antioxidant ascorbic acid (AA) or vitamin C does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB), its oxidized form, dehydroascorbic acid (DHA), enters the brain by means of facilitative transport[1]. |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 389.3±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 170.0±20.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 174.016434 |
| PSA | 100.90000 |
| LogP | -2.32 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | −20°C |