Home
Products
Cytisine
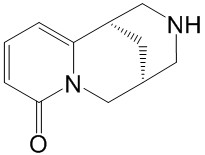


| Product Name | Cytisine |
| Price: | $15 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN02195 |
| CAS No.: | 485-35-8 |
| Molecular Formula: | C11H14N2O |
| Molecular Weight: | 190.24 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Genista tinctoria L. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | O=c1cccc2n1C[C@@H]1CNC[C@H]2C1 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Cytisine is an alkaloid that occurs naturally in several plant genera, such as Laburnum and Cytisus. Cytisine is a partial agonist of α4β2 nAChRs[1], and partial to full agonist at β4 containing receptors and α7 receptors[2]. has been used medically to help with smoking cessation[3]. |
| Target | α4β2 nAChRs[1]. |
| In Vitro | Cytisine (2.5, 5 and 10 mM) is capable of inducing apoptosis in HepG2 cells[4]. Treatment with Cytisine increases the percentage of cells in the sub-G1 phase (P<0.01). The preincubation of HepG2 cells with Cytisine (2.5, 5 and 10 mM) significantly increases the sub-G1 cell population[4]. |
| In Vivo | Cytisine (5 mg/kg, i.p.) eat less and gain less weight than those that receive the vehicle[2]. Total pellet intake increases during Cytisine substitution relative to nicotine and animals self-administered Cytisine significantly less than nicotine[2]. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 413.0±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 203.6±25.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 190.110611 |
| PSA | 34.03000 |
| LogP | 0.07 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |