Home
Products
Imperatorin
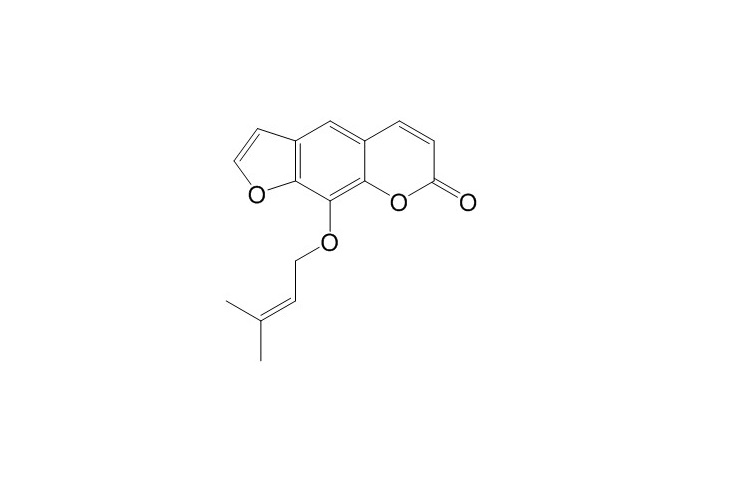


| Product Name | Imperatorin |
| Price: | $23 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN06262 |
| CAS No.: | 482-44-0 |
| Molecular Formula: | C16H14O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 270.3 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Coumarins |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Angelica dahurica Benth. et Hook. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | CC(=CCOc1c2occc2cc2c1oc(=O)cc2)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Imperatorin is an effective of NO synthesis inhibitor (IC50=9.2 μmol), which also is a BChE inhibitor (IC50=31.4 μmol). Imperatorin is a weak agonist of TRPV1 with EC50 of 12.6±3.2 μM. |
| Target | IC50: 9.2 μmol (NO synthesis), 31.4 μmol (BChE)[1]EC50: 12.6±3.2 μM (TRPV1)[2] |
| In Vitro | Imperatorin is a plant secondary metabolite belonging to the coumarins-specifically the furanocoumarins. Imperatorin enhances the GABA-induced chloride ion current (IGABA) through the α1β2γ2S receptors. Imperatorin potentiates IGABA at 100 μmol by 50.5±16.3 % and at 300 μmol by 109.8±37.7 %, respectively. Imperatorin, together with Phellopterin, found in the roots of A. dahurica, inhibit [3H]diazepam binding to the benzodiazepine site of the rat brain GABAA receptor in vitro with an IC50 of 12.3 μmol for Imperatorin and 400 nmol for Phellopterin. Imperatorin, in a concentration ranging from 3.5 to 14 mmol, significantly and irreversibly inhibits GABA-T in a time-dependent and concentration-dependent manner, by irreversibly binding with the active site of GABA-T.Imperatorin is a reversible acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor, and acts in dose-dependent manner. The AChE and BChE inhibitory activities of Imperatorin and a crude extract from the fruits of Angelica archangelica L. is tested by the spectrophotometric method at concentrations of 12.5, 25, 50, and 100 μg/mL. Imperatorin displays low inhibition towards AChE (13.75-46.11 %), whereas it has remarkable inhibitory effect against BChE (37.46-83.98 %). Imperatorin shows selectivity toward BChE rather than AChE, with an IC50 for BChE of 31.4 μmol. Imperatorin, together with (+)-Byakangelicol, are found to be the most effective BACE-1 inhibitors, with IC50s of 91.8 and 104.9 μmol, respectively. Imperatorin (IC50=9.2 μmol) is also effective as an inhibitor of NO synthesis[1]. Imperatorin is a weak agonist of TRPV1, a channel implicated in detecting several noxious stimuli, exhibiting EC50 of 12.6±3.2 μM[2]. |
| In Vivo | At doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg and 30 min after injection, Imperatorin shows an anxiolytic effect and improved different stages of memory and learning processes-both acquisition and consolidation. It is also shown that acute administration Imperatorin at doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg reduced the anxiogenic effect of nicotine (0.1 mg/kg, subcutaneous, s.c.). At 30 and 40 mg/kg, i.p. Imperatorin significantly potentiates the anticonvulsant activity of carbamazepine against maximal electroshock-induced seizures expressed by lowering the ED50 from 10.8 to 6.8 mg/kg (by 34 %) and 6 mg/kg (by 42 %), respectively. Moreover, Imperatorin at 30 mg/kg and carbamazepine at 6.8 mg/kg shows increases the total brain concentration of carbamazepine from 1.260 to 2.328 μg/mL (by 85%), which may be caused by modifying the blood-barrier permeability or acting like an inhibitor of multi-drug resistance proteins[1]. Imperatorin, a naturally occurring furanocoumarin, inactivates gamma-aminobutyric acid transaminase and inhibits acetylcholinesterase activity. Imperatorin administered acutely at the doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg prior to the injection of scopolamine (1 mg/kg) improves memory acquisition and consolidation impaired by scopolamine. Furthermore, repeatable (7 days, twice daily) administration of the highest dose of Imperatorin (10 mg/kg) significantly attenuates the effects of scopolamine on memory acquisition, whereas the doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg of this furanocoumarin are effective when memory consolidation is measured [3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] The experiments are carried out on naive male Swiss mice weighing 20-25 g. Drugs are administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) at the volume of 10 mL/kg. Fresh drug solutions are prepared on each day of experimentation. Control groups receive saline injections of the same volume and via the same route of administration. During the acute treatment, the animals are allocated to the following drug groups: saline, rivastigmine (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.), scopolamine (1 mg/kg, i.p.), Imperatorin (1, 5, 10 mg/kg, i.p.), or Imperatorin coadministered with scopolamine. To measure the memory acquisition processes, scopolamine is administered 20 min before the pretest, whereas Imperatorin and rivastigmine are administered 30 min before the pretest. To measure the memory consolidation processes, rivastigmine or scopolamine (1 mg/kg) is administered immediately after the pretest, whereas Imperatorin is administered 15 min after pretest or after scopolamine injection. On the second day, the mice are retested. In the second set of the experiments, animals are randomly allocated to receive 6 days of i.p. injections of Imperatorin (1, 5, and 10 mg/kg, i.p.) or saline, twice daily (8:00 a.m. and 8:00 p.m.). On the seventh day, these animals are subjected to saline, scopolamine (1 mg/kg, i.p.), Imperatorin (1, 5, and 10 mg/kg, i.p.), or Imperatorin coadministered with scopolamine. To measure the memory acquisition processes, scopolamine is administered 20 min before the pretest and Imperatorin 30 min before the pretest. To measure the memory consolidation processes, scopolamine (1 mg/kg) is administered immediately after the pretest, whereas Imperatorin is administered 15 min after the pretest or after scopolamine injection. On the eighth day, the mice are retested. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 448.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 224.9±28.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 270.089203 |
| PSA | 52.58000 |
| LogP | 3.81 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |