Home
Products
Ellagic acid


| Product Name | Ellagic acid |
| Price: | $18 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN04029 |
| CAS No.: | 476-66-4 |
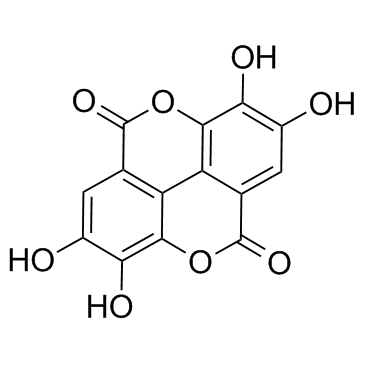
| Molecular Formula: | C14H6O8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 302.2 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Phenols |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The peels of Punica granatum L. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1cc2c(=O)oc3c4c2c(c1O)oc(=O)c4cc(c3O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Ellagic acid is a natural antioxidant, and acts as a potent and ATP-competitive CK2 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 40 nM and a Ki of 20 nM. |
| Target | CK2:40 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Ellagic acid is a potent CK2 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 40 nM and a Ki of 20 nM. Ellagic acid also blocks other kinases such as LYN, PKA, SYK, GSK3, FGR and CK1, with IC50s of 2.9, 3.5, 4.3, 7.5, 9.4 and 13.0 μM, respectively, and shows no obvious effects on DYRK1a, CSK, NPM-ALK, RET and FLT3 (IC50s > 40 μM). Ellagic acid (5-100 μM) shows inhibitory activities against Karpas299, SUDHL1, SR786, and FE-PD cell lines[1]. Ellagic acid (10 μM) exhibits cytotoxic effects on MCF-7 cells after treatment of radiation. Ellagic acid (10 μM) in combination with Irradiation (IR) significantly abridges the capacity of MCF-7 cells to form colonies equated with individual treatments. Ellagic acid with IR also induces cell apoptosis, and facilitates the upregulation of pro-apopttotic Bax and downregulation of Bcl-2 in MCF-7 cells[3]. |
| In Vivo | Ellagic acid (EA; 10 mg/kg/day; p.o., 14 days) strongly decreases MDA brain content by 17%, and reduces the levels of brain TNF-α by 42% in rats. Ellagic acid markedly increases the reduced brain contents of 5-HT (39%), dopamine (DA, 71%), and norepinephrine (NE, 77%). Ellagic acid (10 mg/kg, p.o., 14 days) causes decreased histopathological changes induced by Doxorubicin in rats[2]. |
| Cell Assay | ALCL cell viability is measured by MTT assay. Briefly, 0.1 × 105 cells are seeded onto 96-well microculture plates 12 hrs before adding ellagic acid. The cells are grown in 200 µL of complete RPMI-1640 medium, under standard tissue-culture conditions, in the presence or absence of the drug (Ellagic acid) for 48 hours. Twenty µL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) are then added to the cell suspension for 4h. The intracellular formazan crystals are dissolved with 150 µL of DMSO and optical density, measured on a spectrophotometer at 540 nm, represents the mean (± SD) of triplicate cultures[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Fifty male adult Sprague-Dawley rats are divided randomly into five groups as follow: Group (1) receives corn oil orally as a vehicle and served as normal control. Group (2) receives doxorubicin (DOX) injection (5 mg/kg, i.p.) twice a week for 14 days. Group (3) receives Ellagic acid (10 mg/kg, p.o.; daily) for 14 days and DOX (5 mg/kg, i.p.) twice a week for 14 days. Group (4) receives rosmarinic acid (RA; 75 mg/kg, p.o.; daily) for 14 days and DOX (5 mg/kg, i.p.) twice a week for 14 days. Group (5) receives Ellagic acid (10 mg/kg, p.o.; daily) with RA (75 mg/kg, p.o.; daily) for 14 days and DOX injection (5 mg/kg, i.p.) twice a week for 14 days[2]. |
| Density | 2.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 796.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 310.1±26.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 302.006256 |
| PSA | 141.34000 |
| LogP | 0.52 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |