Home
Products
IPA-3
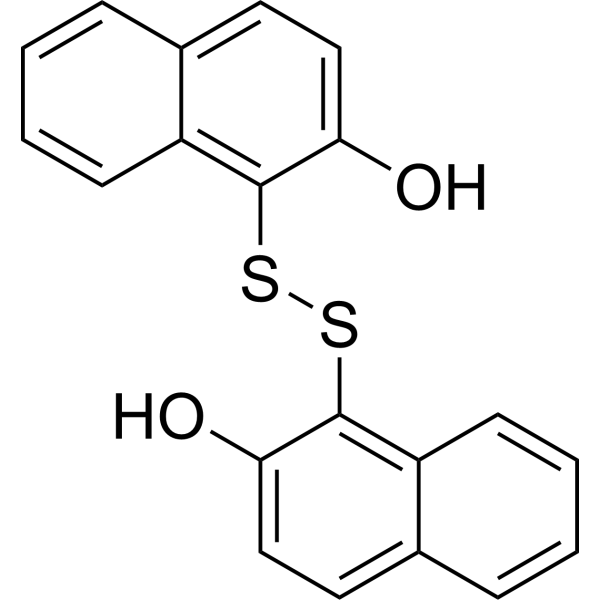


| Product Name | IPA-3 |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00225 |
| CAS No.: | 42521-82-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C20H14O2S2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 350.45 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1ccc2c(c1SSc1c(O)ccc3c1cccc3)cccc2 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | IPA-3 is a selective non-ATP competitive PAK1 inhibitor with IC50 of 2.5 μM, and shows no inhibition to group II PAKs (PAKs 4-6). |
| Target | PAK1:2.5 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | IPA-3 inhibits Pak1 activation in part by binding covalently to the regulatory domain of Pak1. IPA-3 binds Pak1 covalently in a time- and temperature-dependent manner. IPA-3 prevents binding of the Pak1 activator Cdc42. IPA-3 binds directly to the Pak1 autoregulatory domain. IPA-3 reversibly inhibits PMA-induced membrane ruffling in cells[1]. IPA-3 (2 µM, 5 µM or 20 µM) reduces cell spreading in human primary Schwann and schwannoma cells. IPA-3 treatment significantly reduces the number of adherent Schwann and schwannoma cells in a dose-dependent manner[2]. IPA-3 is a non ATP-competitive, allosteric inhibitor of p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1). PIR3.5 is the control compound of IPA-3. IPA-3 prevents Cdc42-stimulated Pak1 autophosphorylation on Thr423. IPA-3 also prevents sphingosine-dependent Pak1 autophosphorylation. IPA-3 does not target exposed cysteine residues on Pak1. The disulfide bond of IPA-3 is critical for inhibition of Pak1 and in vitro reduction by the reducing agent dithiothreitol (DTT) abolishes Pak1 inhibition by IPA-3. IPA-3 inhibits activation of Pak1 by diverse activators, but does not inhibit preactivated Pak1. IPA-3 inhibits PDGF-stimulated Pak activation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Human primary schwannoma cells are grown on 96 well plates for 2 days. Cells are left untreated or treated with 5 µM IPA-3, 20 µM IPA-3 or 20 µM PIR-3.5 for 24 hours. The MTS-solution is left on the cells for 3 hours, before the absorbance at 490 nm is measured. The experiments are conducted three times and mean and standard error of the mean is calculated with Excel. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 543.7±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 263.4±24.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 350.043518 |
| PSA | 91.06000 |
| LogP | 4.96 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |