Home
Products
Irisflorentin
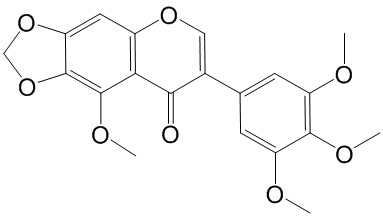


| Product Name | Irisflorentin |
| Price: | $37 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN05478 |
| CAS No.: | 41743-73-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C20H18O8 |
| Molecular Weight: | 386.35 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Yellow powder |
| Source: | The rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis (L.) DC. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | COc1cc(cc(c1OC)OC)c1coc2c(c1=O)c(OC)c1c(c2)OCO1 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Irisflorentin, a naturally occurring isoflavone, is an abundant active constituent in Rhizoma Belamcandae. Irisflorentin markedly reduces the transcriptional and translational levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) as well as the production of NO. Anti-inflammatory activity[1]. |
| In Vitro | Irisflorentin does not affect the LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages viability up to a concentration of 40 μM[1]. Irisflorentin (10-40 μM) inhibits the LPS-induced production of NO in a concentration-dependent manner without affecting the iNOS activity in RAW 264.7 macrophages[1]. Irisflorentin (10-40 μM) concentration dependently inhibits the LPS (10 ng/mL)-induced increase in iNOS mRNA expression in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Irisflorentin (10-40 μM) concentration-dependently suppresses the production of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages[1]. Irisflorentin (10-40 μM) concentration dependently inhibits the LPS (10 ng/mL)-induced increase in iNOS protein levels. Irisflorentin (10-40 μM) concentration-dependently suppresses LPS-induced p38 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner, but slightly affects JNK phosphorylation[1]. RT-PCR[1] Cell Line: LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages Concentration: 10, 20, 40 μM Incubation Time: Result: Inhibited the LPS (10 ng/mL)-induced increase in iNOS mRNA expression. Suppressed the production of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages Concentration: 10, 20, 40 μM Incubation Time: Result: Inhibited the LPS (10 ng/mL)-induced increase in iNOS protein levels. Suppressed LPS-induced p38 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation, but slightly affected JNK phosphorylation. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 569.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 250.5±30.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 386.100159 |
| PSA | 85.59000 |
| LogP | 3.19 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |