Home
Products
CHIR-124
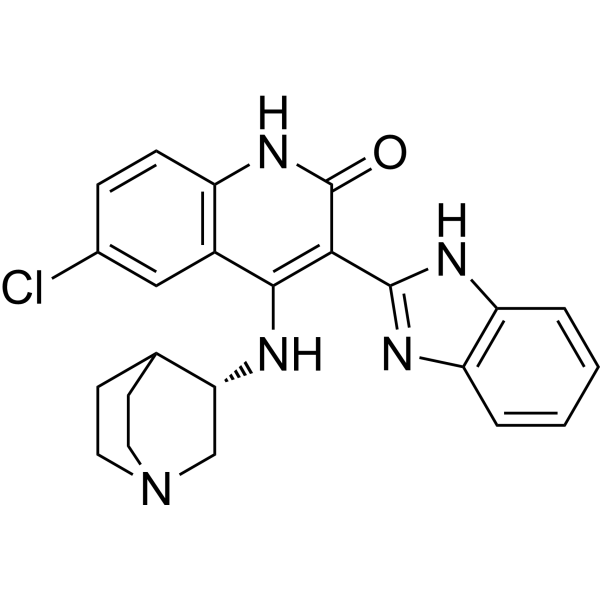


| Product Name | CHIR-124 |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00231 |
| CAS No.: | 405168-58-3 |
| Molecular Formula: | C23H22ClN5O |
| Molecular Weight: | 419.91 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Clc1ccc2c(c1)c(N[C@@H]1CN3CCC1CC3)c(c(=O)[nH]2)c1nc2c([nH]1)cccc2 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | CHIR-124 is a potent and selective Chk1 inhibitor with IC50 of 0.3 nM, and also potently targets PDGFR and FLT3 with IC50s of 6.6 nM and 5.8 nM. |
| Target | Chk1:0.3 nM (IC50) Chk2:697.4 nM (IC50) PDGFR:6.6 nM (IC50) FLT3:5.8 nM (IC50) Cdk4/cyclin D:2.05 μM (IC50) CDC2/cyclin B:0.5057 μM (IC50) Cdk2/cyclin A:0.1911 μM (IC50) bFGFR:2.01 μM (IC50) FGFR3:1.29 μM (IC50) VEGFR2 FLK1:0.5779 μM (IC50) VEGFR1 FLT1:0.4636 μM (IC50) PKCα:0.58 μM (IC50) PKAβ I:2.25 μM (IC50) PKCβ II:0.58 μM (IC50) PKCγ:0.11 μM (IC50) ERK2:4.31 μM (IC50) PKA:0.1031 μM (IC50) GSK3:0.0233 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | CHIR-124 is 500- to 5,000-fold less active against other cell cycle kinases, such as cyclin-dependent kinase 2/cyclin A (0.19 μM), cdc2/cyclin B (0.51 μM), and cyclin-dependent kinase 4/cyclin D (2.1 μM). CHIR-124 (≥0.9 nM) in combination with SN-38 (≥0.42 nM) causes significant synergy or >10% deviation from additivity in human cancer cell lines expressing mutant p53, and these values overlap and fall below the IC50s for SN-38 (1.2×10-7 M) and CHIR-124 (2.2×10-7 M), respectively. Moreover, CHIR-124 (100 nM) abrogates the SN-38-induced S and G2-M phase cell cycle checkpoints. CHIR-124 (200 nM) leads to a 2.5-fold elevated level of cdc25A above that of the untreated HCT116 p53−/− cells. The down-regulation of cdc25A induced by SN-38 is completely restored by concurrent or sequential treatment with CHIR-124, proving that CHIR-124 inhibits the Chk1-mediated destruction of cdc25A in whole cells[1]. CHIR-124 occupies the ATP-binding site, inhibits Chk1 (IC50, 0.3 nM) 2,000-fold more potently than Chk2 (IC50, 0.7 μM)[2]. |
| In Vivo | CHIR-124 (10 or 20 mg/kg, p.o.) does not have a significant effect on tumor growth when compared with the vehicle-treated group, but it potentiates the growth inhibitory effect of CPT-11 in a human breast carcinoma xenograft model. The potentiation of the tumor growth inhibitory effect of CPT-11 by CHIR-124 is associated with an increase in apoptosis induction in the tumors. CHIR-124 reverses the suppression of phospho-H3 staining induced by CPT-11, indicating abrogation of the G2-M checkpoint by CHIR-124[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Severe combined immunodeficient mice harboring MDA-MD-435 tumor xenografts are randomized into the following treatment groups of 10: vehicle (captisol) alone, 5 mg/kg CPT-11, 10 mg/kg CHIR-124, 20 mg/kg CHIR-124, 5 mg/kg CPT-11 plus 10 mg/kg CHIR-124, or 5 mg/kg CPT-11 plus 20 mg/kg CHIR-124. Treatment is initiated on the day after randomization (day 1). CPT-11 is given i.p. daily (four times daily) ×5 on days 1 to 5, whereas CHIR-124 is given orally four times daily ×6 on days 2 to 7 in captisol. Percent tumor growth inhibition is defined as % T/C, where T = the treatment group mean, and C = the control group mean. In a similar study, tumors harvested from mice sacrificed on day 4 of treatment are examined for apoptosis by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick-end labeling staining and for mitotic index by immunofluorescence labeling with phospho-histone H3 antibody. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Exact Mass | 419.151276 |
| PSA | 76.28000 |
| LogP | 3.86 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |