Home
Products
Retinoic acid
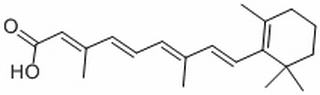


| Product Name | Retinoic acid |
| Price: | $15 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN08822 |
| CAS No.: | 302-79-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C20H28O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 300.44 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Diterpenoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Yellow powder |
| Source: | From lamb liver |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | CC(=CC=CC(=CC(=O)O)C)C=CC1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Retinoic acid is a metabolite of vitamin A that plays important roles in cell growth, differentiation, and organogenesis. Retinoic acid is a natural agonist of RAR nuclear receptors, with IC50s of 14 nM for RARα/β/γ. Retinoic acid bind to PPARβ/δ with Kd of 17 nM. |
| Target | PPARβ/δ:17 nM (Kd) PPARα:103 nM (Kd) PPARγ:178 nM (Kd) RARα:14 nM (IC50) RARβ:14 nM (IC50) RARγ:14 nM (IC50) Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Retinoic acid (All-trans-retinoic acid, ATRA) is a highly potent derivative of vitamin A that is required for virtually all essential physiological processes and functions because of its involvement in transcriptional regulation of over 530 different genes. Retinoic acid exerts its actions by serving as an activating ligand of nuclear retinoic acid receptors (RARα-γ), which form heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRα-γ)[1]. Retinoic acid (RA) bound to PPARα and PPARγ with a low affinity demonstrated by Kd values of 100-200 nM. In contrast, Retinoic acid associates with PPARβ/δ with a Kd of 17 nM, revealing both high affinity and isotype selectivity[2]. Undifferentiated P19 cells express the Retinoic acid (RA) receptors RARα, RARβ, RARγ, and PPARβ/δ, as well as the Retinoic acid -binding proteins CRABP-II and FABP5. Induction of differentiation by treatment of cells with Retinoic acid results in transient up-regulation of CRABP-II and down-regulation of FABP5 that are observed at the level of both the respective proteins and mRNAs. Following the initial decrease, the level of both FABP5 protein and mRNA increases to attain a 2-2.5-fold higher level in mature neurons as compared with undifferentiated P19 cells. Induction of differentiation does not markedly affect the levels of either RARα or PPARβ/δ. The level of RARγ mRNA decreases by about 5-fold by day 4 and remained low in mature neurons[3]. Retinoic acid (RA) is a morphogen derived from retinol (vitamin A) that plays important roles in cell growth, differentiation, and organogenesis. The Retinoic acid interacts with retinoic acid receptor (RAR) and retinoic acid X receptor (RXR) which then regulate the target gene expression[4]. |
| Cell Assay | P19 cell are induced to undergo neuronal differentiation according to established procedures. Briefly, cells are cultured on 1% agarose-coated 10 cm dishes at 3×10 5 cells/mL in α-minimal essential medium supplemented with 10% FBS. Differentiation is induced by addition of Retinoic acid (1 μM) and medium containing Retinoic acid replaced 2 days later. On day 4, cell aggregates are collected by centrifugation, separated to single cells by trypsin/EDTA treatment, replated onto poly-L-lysine-coated plates, and cultured in α-minimal essential medium supplemented with 10% FBS. On day 6, medium is replaced with neurobasal medium containing B27 supplement and 2 mM GlutaMAX. Medium is replaced every 2 days for an additional week[3]. |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 462.8±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 350.6±11.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 300.208923 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.83 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |