Home
Products
Farrerol
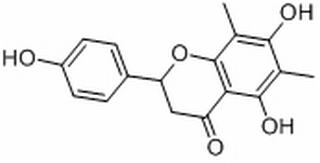


| Product Name | Farrerol |
| Price: | $62 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN05183 |
| CAS No.: | 24211-30-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C17H16O5 |
| Molecular Weight: | 300.3 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Flavonoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The leaves of Rhododendron dauricum L. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | Oc1ccc(cc1)C1CC(=O)c2c(O1)c(C)c(c(c2O)C)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Farrerol is a bioactive constituent of Rhododendron, with broad activities such as anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, neuroprotective and hepatoprotective effects[1][2][3][4][5][6]. |
| In Vitro | Farrerol observably reduces the production of inflammatory mediators including IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and iNOS in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells via suppressing AKT, ERK1/2, JNK1/2, and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation[1]. Farrerol attenuates β-amyloid-induced oxidative stress and inflammation through Nrf2/Keap1 pathway in a microglia cell line[2]. Farrerol inhibits angiogenesis through Akt/mTOR, Erk and Jak2/Stat3 signal pathway[3]. Farrerol overcomes the invasiveness of lung squamous cell carcinoma cells by regulating the expression of inducers of epithelial mesenchymal transition[4]. Farrerol ameliorates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via activation of Nrf2 and autophagy[6]. |
| In Vivo | Farrerol protects dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinson's disease by suppressing the activation of the AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways[5]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 583.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 219.7±23.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 300.099762 |
| PSA | 86.99000 |
| LogP | 4.11 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2~8℃ |