Home
Products
18alpha-Glycyrrhetinic acid
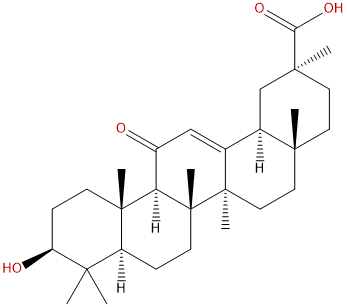


| Product Name | 18alpha-Glycyrrhetinic acid |
| Price: | $60 / 10mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN07193 |
| CAS No.: | 1449-05-4 |
| Molecular Formula: | C30H46O4 |
| Molecular Weight: | 470.7 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Triterpenoids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The roots of Glycyrrhize glabra L. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | O=C1C=C2[C@H]3C[C@](C)(CC[C@]3(C)CC[C@]2([C@]2([C@H]1[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@H](C(C1CC2)(C)C)O)C)C)C(=O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid, a diet-derived compound, is an inhibitor of NF-kB and an activator of proteasome, which serves as pro-longevity and anti-aggregation factor in a multicellular organism. 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces apoptosis[1][2]. |
| Target | NF-κB Proteasome |
| In Vitro | 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid (18a-GA) markedly reduces LX-2 cell numbers by 14.8% and 31.2% after 48 h and 72 h of treatment, respectively (P< 0.05). 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid also significantly increases the percentage of LX-2 cells in phase G0/G1 and decreases it in phase S after treated for 48 h and 72 h compare with the control group. 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid increases apoptosis to 6.8% at 48 h, compare with control (2.5%), and at 72 h the percentages of apoptotic cells in control and the treatment groups are 3.1% and 15.6%, respectively, in LX-2 cells (P<0.01). Furthermore, 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces expression of PPAR-γ and alters some cell cycle and apoptosis-related proteins. 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid also inhibits NF-κB DNA-binding activity[1]. |
| In Vivo | 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid (18α-GA) treatment significantly enhances life span of C. elegans strains with the most effective concentration being 20 μg/mL. Results reveal a significant delay of paralysis upon 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid treatment. 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid treatment also confers a significant reduction of Aβ deposits[2]. |
| Cell Assay | For the determination of cell cycle, 5×105 cells per well are seeded onto 6-well plates and incubated overnight in complete growth medium (DMEM+10% FBS). After starvation for 24 h, the cells are subsequently stimulated with 10% FBS with or without the presence of 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid (18a-GA). The final concentration of 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid is 8.0 mM. The cells are incubated for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, respectively, and then the flow cytometric analysis is performed. Flow cytometric analysis is performed in triplicate. After being treated with 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid, the cells are stained and then cell apoptosis status is measured by flow cytometry[1]. |
| Animal Admin | C. elegans strains are used in this study. Synchronized L4 larvae CL2006 animals (100 to 120 animals per condition) are transferred to nematode growth medium (NGM) plates containing either 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid (18α-GA) or DMSO at 20°C. Synchronized CL4176 animals (150 to 300 animals per condition) are transferred to NGM plates containing either 18α-Glycyrrhetinic acid or DMSO at 16°C for 48 h before temperature upshift to 25°C for transgene induction. Scoring of paralyzed animals is initiated at day 1 of adulthood for CL2006 strain and 24 h after temperature upshift for CL4176 strain. Each paralysis assay is repeated at least thrice. Nematodes are scored as paralyzed if they exhibit halos of cleared bacteria around their heads or fail to undergo half end body wave propagation upon prodding[2]. |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 588.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 323.7±26.6 °C |
| Exact Mass | 470.339600 |
| PSA | 74.60000 |
| LogP | 6.57 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |