Home
Products
Zeaxanthin
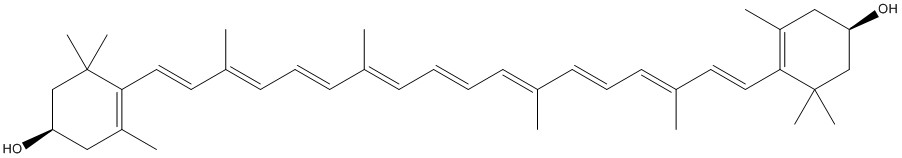


| Product Name | Zeaxanthin |
| Price: | $89 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN06599 |
| CAS No.: | 144-68-3 |
| Molecular Formula: | C40H56O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 568.88 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Miscellaneous |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The fruits of Zea mays L. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | O[C@@H]1CC(=C(C(C1)(C)C)/C=C/C(=C/C=C/C(=C/C=C/C=C(/C=C/C=C(/C=C/C1=C(C)C[C@H](CC1(C)C)O)C)C)/C)/C)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Zeaxanthin, a diet-obtained carotenoid, presents in the macula region of the eye. Zeaxanthin shows antioxidant effects[1][2]. |
| In Vitro | Much of the Lutein and Zeaxanthin in the leaves of plants is protein-bound.In fruits and flower petals, the xanthophylls are esterified and are concentrated into chromoplasts where they are found to be solubilized in the membranes. In humans and higher animals, Lutein and Zeaxanthin are accumulated in lipophilic tissues such as adipose tissue and are carried in the blood by the lipoproteins, probably in a nonspecific manner similar to cholesterol. Lutein and Zeaxanthin are distributed equally between LDL and HDL fractions in human blood, in contrast to the hydrocarbon carotenoids that are preferentially found in LDL fractions, up to 75%[3]. |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 711.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 273.4±26.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 568.428040 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 11.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | −20°C |