Home
Products
JNK-IN-8


| Product Name | JNK-IN-8 |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00447 |
| CAS No.: | 1410880-22-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C29H29N7O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 507.59 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
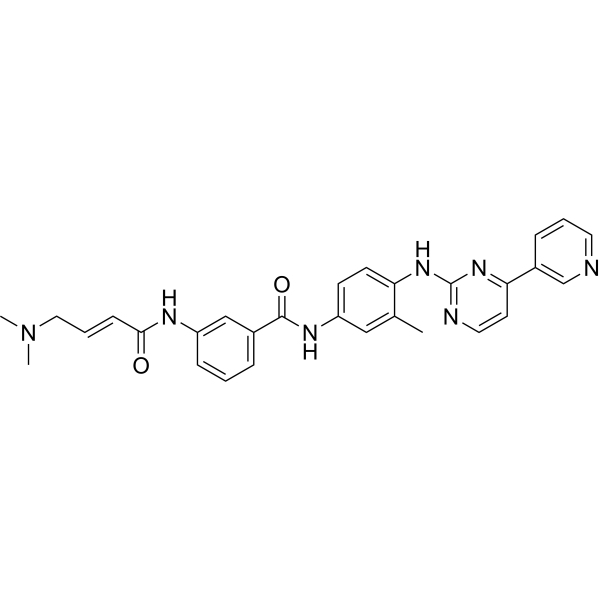
| SMILES: | CN(CC=CC(=O)Nc1cccc(c1)C(=O)Nc1ccc(c(c1)C)Nc1nccc(n1)c1cccnc1)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | JNK-IN-8 is a potent JNK inhibitor with IC50s of 4.7 nM, 18.7 nM, and 1 nM for JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3, respectively. |
| Target | JNK3:1 nM (IC50) JNK1:4.7 nM (IC50) JNK2:18.7 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | JNK-IN-8 inhibits phosphorylation of c-Jun, a direct substrate of JNK kinase. JNK-IN-8 inhibits c-Jun phosphorylation in HeLa and A375 cells with EC50 of 486 nM and 338 nM, respectively. JNK-IN-8 also exhibits exceptional selectivity based upon KinomeScan and enzymatic profiling. Cumulatively these combined profiling technologies demonstrate that both JNK-IN-8 and JNK-IN-12 are remarkably selective covalent JNK inhibitors and are appropriate for interrogating JNK-dependent biological phenomena[1]. JNK-IN-8, a selective pan-JNK inhibitor, is discovered to inhibit JNK kinase by broad-base kinase selectivity profiling of a library of acrylamide kinase inhibitors based on the structure of imatinib using the KinomeSca approach. JNK-IN-8 possess distinct regio-chemistry of the 1,4-dianiline and 1,3-aminobenzoic acid substructures relative to imatinib and uses an N,N-dimethyl butenoic actemide warhead to covalently target Cys154. JNK-IN-8 adopts an L-shaped type I binding conformation to access Cys 154 located towards the lip of the ATP-binding site[2]. |
| Cell Assay | HEK-293 cells stably expressing Interleukin Receptor 1 (HEK293-IL1R) are cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM glutamine and 1×antimycotic/antibiotic solution. Cells are serum starved for 18 h before incubation with DMSO or JNK-IN-8, stimulated with 2 μM Anisomycin for 1h and lysates are clarified by centrifugation for 10 min at 16000 g and 4°C[1]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Exact Mass | 507.238281 |
| PSA | 115.63000 |
| LogP | 2.79 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |