Home
Products
Bisindolylmaleimide I (GF109203X)
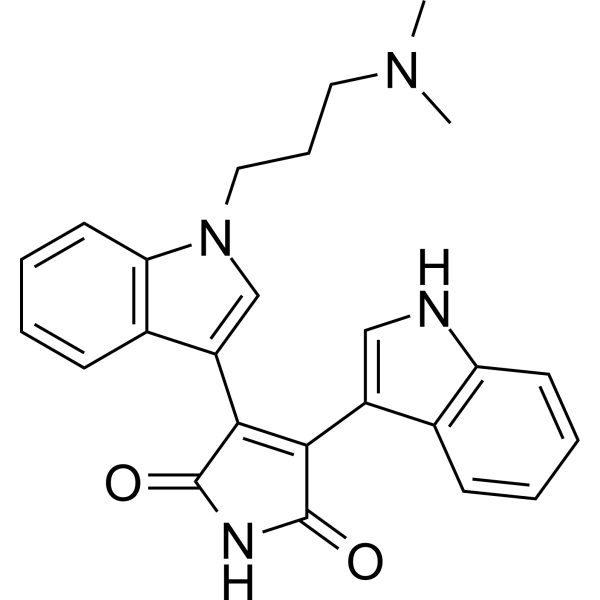


| Product Name | Bisindolylmaleimide I (GF109203X) |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00454 |
| CAS No.: | 133052-90-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C25H24N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 412.48 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | CN(CCCn1cc(c2c1cccc2)C1=C(C(=O)NC1=O)c1c[nH]c2c1cccc2)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Bisindolylmaleimide I (GF109203X) is a highly selective, cell-permeable, and reversible protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor with a Ki of 14 nM. |
| Target | Bovine brain PKC:10 nM (IC50) PKCβII:16 nM (IC50) PKCβI:17 nM (IC50) PKCα:20 nM (IC50) PKCγ:20 nM (IC50) FDGFR:65 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Bisindolylmaleimide I is a competitive inhibitor with respect to ATP (Ki=14 nM) and displays high selectivity for PKC as compared to five different protein kinases. GF 109203X efficiently prevents PKC-mediated phosphorylations of an Mr=47,000 protein in platelets and of an Mr=80,000 protein in Swiss 3T3 cells. GF 109203X inhibits collagen- and a-thrombin-induced platelet aggregation as well as collagen-triggered ATP secretion. However, ADP-dependent reversible aggregation is not modified. In Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts, GF 109203X reverses the inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding induced by phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and prevents [3H] thymidine incorporation into DNA, only when this is elicited by growth promoting agents which activate PKC[1]. |
| In Vivo | Pial arteriole diameter changes are monitored using a closed cranial window in vivo microscopy technique. The pial arteriole dilatory response associated with SNS is decreased by 45%, when comparing DM vs either ND or TR rats. Also, pial arteriolar dilations to topical KCl and NS1619 are largely attenuated in DM rats, but not in ND or TR animals. These responses are completely restored by the acute application of Bisindolylmaleimide I to the brain surface. The PKC inhibitor has no effect on vascular responses in normoglycemic and TR animals. In conclusion, DM-associated chronic impairment of neurovascular coupling may be readily reversed by a PKC-α/β/γ inhibitor or prevented via pancreatic islet transplantation. Specific PCK isoforms (α/β/γ) are believed to be mechanistically linked to the neurovascular uncoupling seen with hyperglycemia[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Three sets of Lewis rats is used for this study: 1) euglycemic 4–6 month old non-diabetic controls (ND group, n=11); 2) streptozotocin (STZ)-treated diabetic rats (6 month old, 4 months post-STZ) (DM group, n=6); and 3) STZ-treated diabetic animals, subjected to pancreatic islet transplantation soon after the establishment of the diabetic model, studied 100–110 days after the transplant (TR group, n=7)[2]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 685.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 368.5±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 412.189911 |
| PSA | 70.13000 |
| LogP | 3.88 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |