Home
Products
BAPTA-AM


| Product Name | BAPTA-AM |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00459 |
| CAS No.: | 126150-97-8 |
| Molecular Formula: | C34H40N2O18 |
| Molecular Weight: | 764.68 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
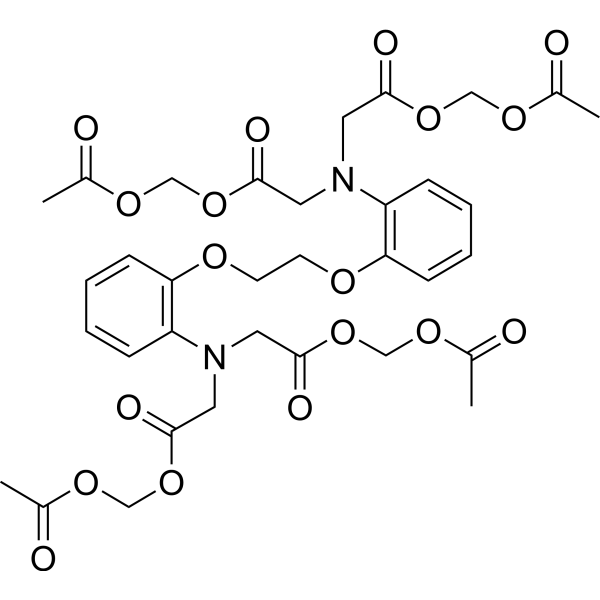
| SMILES: | O=C(CN(c1ccccc1OCCOc1ccccc1N(CC(=O)OCOC(=O)C)CC(=O)OCOC(=O)C)CC(=O)OCOC(=O)C)OCOC(=O)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | BAPTA-AM is an intracellular calcium chelator. |
| Target | calcium chelator[1] |
| In Vitro | The permeable calcium chelator BAPTA/AM is known to prevent free radical-mediated toxicity promote apoptosis in non-neuronal cells and produce a beneficial effect in neuronal cells by protecting neurons from ischemic damage. In addition, it has been suggested that BAPTA/AM induces a late, but not early, increase of intracellular calcium in I-IL-60 neoplastic cells. Mixed cortical cell cultures (DIV 13-16) exposed to 10μM BAPTA/AM for 24- or 48-hr show moderate (45-70%) neuronal injury as evaluated by increased LDH release into the bathing medium after 24-48-hr. Exposure of cortical cultures to 3-10 μM BAPTA/AM for 48-hr evoke dose-dependent neuronal damage[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Neuronal injury is quantitatively estimated by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released from damaged cells into the bathing medium 24- or 48-hr after the 10 μM BAPTA/AM treatment. The morphological findings are confirmed by staining with neuron-specific enolase (NSE) antibody and tryphan blue[1]. |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 796.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 435.3±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 764.227600 |
| PSA | 235.34000 |
| LogP | 2.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | −20°C |