Home
Products
XMD8-92
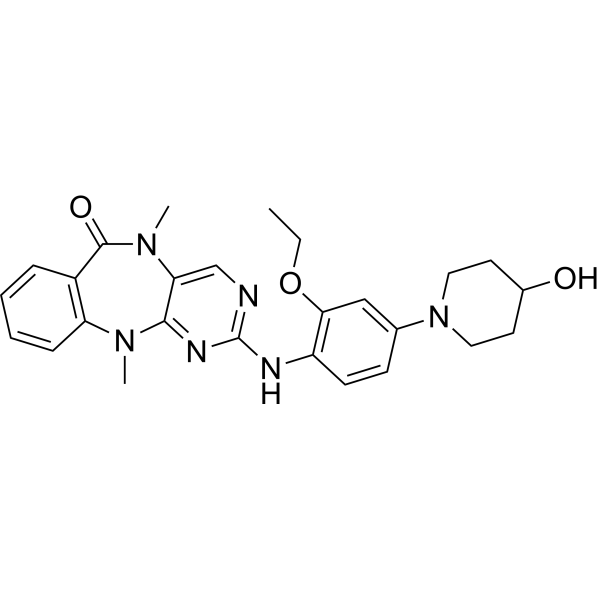


| Product Name | XMD8-92 |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN00155 |
| CAS No.: | 1234480-50-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C26H30N6O3 |
| Molecular Weight: | 474.55 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | CCOc1cc(ccc1Nc1ncc2c(n1)n(C)c1ccccc1c(=O)n2C)N1CCC(CC1)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | XMD8-92 is a highly selective ERK5/BMK1 inhibitor with dissociation constant (Kd) value of 80 nM. |
| Target | BMK1:80 nM (Kd) |
| In Vitro | XMD8-92 exhibits the greatest affinity towards BMK1 with a measured dissociation constant (Kd) of 80 nM, while DCAMKL2, TNK1 and PLK4 exhibit Kd’s of 190, 890 and 600 nM, respectively. XMD8-92 is profiled against all detectable kinases in HeLa cell lysates using the KiNativ method and is found to be about 10-fold more selective for BMK1 with a IC50 of 1.5 μM than the most potent off-targets, TNK1 (IC50=10 μM) and ACK1 (aka TNK2, IC50=18 μM). Other weak off-targets include the kinase domain 2 of RSK1 and RSK2, PIK4A and PIK4B, and FAK. Notably, MEK5 is not significantly inhibited by XMD8-92 at up to 50 μM[1]. XMD8-92 shows high selectivity to BMK1 in an in vitro ATP-site competition binding assay against 402 kinases as well as in the KiNativ method against all detectable kinases in HeLa cell lysates. XMD8-92 blocks EGF-induced activation of BMK1 with IC50 of 240 nM and, with concentration as high as 5 μM, XMD8-92 has no inhibitory effect on ERK1/2 activation by EGF[2]. |
| In Vivo | XMD8-92 significantly inhibits tumor growth in vivo by 95%. The pharmacokinetics of XMD8-92 is evaluated in Sprague-Dawley rats given a single intravenous or oral dose. XMD8-92 is found to have a 2.0 hr half life clearance of 26 mL/min/kg. XMD8-92 has moderate tissue distribution with a calculated volume of distribution of 3.4 L/kg. XMD8-92 has high oral bioavailability with 69% of the dose absorbed. After a single oral dose of 2 mg/kg, maximal plasma concentrations of approximately 500 nM are observed by 30 minutes, with 34 nM remaining 8 hr post dose. In tolerability experiments, high plasma concentrations of drug (approximately 10 μM following IP dosing of 50 mg/kg) are maintained throughout the 14 days. XMD8-92 appeares to be well tolerated and the mice appeared healthy with no sign of distress. No vasculature instability is observed in the XMD8-92-treated mice[1]. XMD8-92 treatment in both immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice blocked the growth of lung and cervical xenograft tumors, respectively, by 95%. This remarkable anti-tumor effect of XMD8-92 in lung and cervical xenograft tumor models is due to XMD8-92’s capacity to inhibit tumor cell proliferation through the PML suppression-inducted p21 checkpoint protein, and by blocking of BMK1’s contribution in tumor-associated angiogenesis. Besides, BMK1 knockout (KO) in mice leads to complete and irreversible removal of the BMK1 protein, while XMD8-92 treatment in mice only suppresses the activity of BMK1, which is reversible. Second, the vasculature instability observed in BMK1 KO mice may be due to lack of the C-terminal non-kinase domain of BMK1, which is still present during XMD8-92 treatment of animals[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[1] 5×105 HeLa cells are resuspended in DMEM and injected subcutaneously into the right flank of 6-week-old Nod/Scid mice (day 0). On the second day (day 1) after tumor cell injection, mice are randomized into 2 groups (6 animals, XMD8-92, 1-28 day, and 18 animals, control). The XMD8-92 (1-28 day) group is treated with XMD8-92 at the dose of 50 mg/kg twice a day intraperitoneally. The control group receive daily injections of the carrier solution as control. On the day 7, the control group is randomized into 2 groups (6 animals, XMD8-92, 7-28 day, and 12 animals, control). And on the day 14, the remaining control group is randomized into 2 groups (6 animals, XMD8-92, 14-28 day, and 6 animals, control). Treatment with XMD8-92 in XMD8-92 (7-28 day) and XMD8-92 (14-28 day) groups is initiated on day 7 and day 14, respectively. Tumor size is measured using a caliper, and tumor volume is determined[1]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 741.8±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 402.4±35.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 474.237946 |
| PSA | 97.44000 |
| LogP | 1.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |