Home
Products
3,4-Dihydrocoumarin
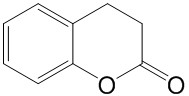


| Product Name | 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin |
| Price: | $23 / 20mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN06121 |
| CAS No.: | 119-84-6 |
| Molecular Formula: | C9H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 148.2 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Coumarins |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The leaves of Southern sweet-grass. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: | O=C1CCc2c(O1)cccc2 |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Dihydrocoumarin is a compound found in Melilotus officinalis. Dihydrocoumarin is a yeast Sir2p inhibitor. Dihydrocoumarin also inhibits human SIRT1 and SIRT2 with IC50s of 208 μM and 295 μM, respectively[1]. |
| Target | hSIRT1:208 μM (IC50) hSIRT2:295 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Dihydrocoumarin induces a concentration-dependent inhibition of SIRT1 (IC50 of 208 μM) in an in vitro enzymatic assay. A decrease in SIRT1 deacetylase activity is observed even at micromolar doses (85±5.8 and 73±13.7% activity at 1.6 μM and 8 μM, respectively). The microtubule SIRT2 deacetylase is also inhibited with a similar dose dependency (IC50 of 295 μM)[1]. Dihydrocoumarin (1-5 mM) increases cytotoxicity in the TK6 cell line in a dose-dependent manner following a 24-h exposure. Dihydrocoumarin (1-5 mM) increases apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner in the TK6 cell line at the 6-h time point. A 5-mM dose of Dihydrocoumarin increases apoptosis at the 6-h time point in the TK6 cell line[1]. Dihydrocoumarin (1-5 mM) increases p53 lysine 373 and 382 acetylation in a dose-dependent manner in the TK6 cell line following a 24-h exposure period[1]. |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 272.0±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 108.4±17.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 148.052429 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 1.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |