Home
Products
Trimethylamine oxide


| Product Name | Trimethylamine oxide |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN01852 |
| CAS No.: | 1184-78-7 |
| Molecular Formula: | C3H9NO |
| Molecular Weight: | 75.11 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Alkaloids |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The headspace of heated menhaden fish oil. |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
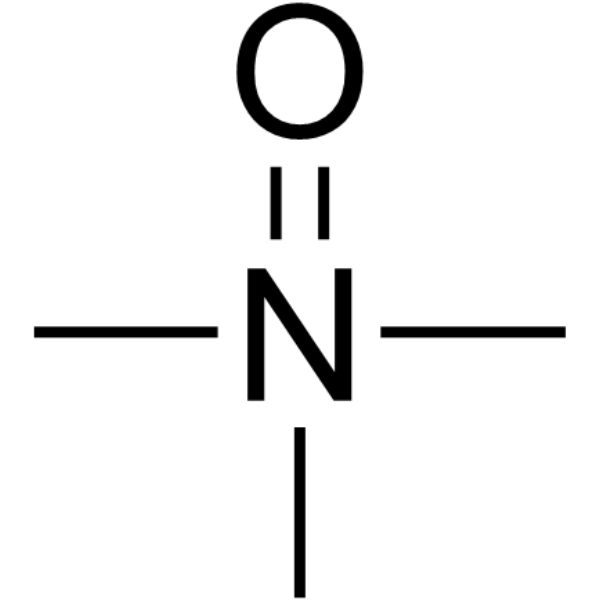
| SMILES: | [O-][N+](C)(C)C |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Trimethylamine N-oxide is a gut microbe-dependent metabolite of dietary choline and other trimethylamine-containing nutrients. Trimethylamine N-oxide induces inflammation by activating the ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome. Trimethylamine N-oxide also accelerates fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation and induces cardiac fibrosis by activating the TGF-β/smad2 signaling pathway[1][2][3]. |
| Target | ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome[1] TGF-β/smad2[1] |
| In Vitro | The size and migration of fibroblasts are increased after Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) treatment compared with non-treated fibroblasts in vitro. Trimethylamine N-oxide increases TGF-β receptor I expression, which promotes the phosphorylation of Smad2 and up-regulates the expression of α-SMA and collagen I. The ubiquitination of TGF-βRI is decreased in neonatal mouse fibroblasts after Trimethylamine N-oxide treatment. Trimethylamine N-oxide also inhibits the expression of smurf2[2]. Trimethylamine N-oxide is frequently found in the tissues of a variety of marine organisms that protects against the adverse effects of temperature, salinity, high urea and hydrostatic pressure[3]. |
| In Vivo | Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) contributes to cardiovascular diseases by promoting inflammatory responses. C57BL/6 mice are fed a normal diet, high-choline diet and/or 3-dimethyl-1-butanol (DMB) diet. The levels of Trimethylamine N-oxide and choline are increased in choline-fed mice. Left ventricular hypertrophy, pulmonary congestion, and diastolic dysfunction are markedly exacerbated in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) mice fed high-choline diets compared with mice fed the control diet. Myocardial fibrosis and inflammation were markedly increased in HFpEF mice fed high-choline diets compared with animals fed the control diet[1]. |
| Density | 0.9301 (rough estimate) |
| Boiling Point | 133.8°C (rough estimate) |
| Exact Mass | 75.068413 |
| PSA | 29.43000 |
| LogP | -2.57 |