Home
Products
Dehydrojuncusol
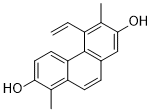


| Product Name | Dehydrojuncusol |
| Price: | $424 / 5mg |
| Catalog No.: | CN03413 |
| CAS No.: | 117824-04-1 |
| Molecular Formula: | C18H16O2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 264.3 g/mol |
| Purity: | >95% |
| Type of Compound: | Phenols |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The stems of Juncus effusus L. |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
| SMILES: |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Dehydrojuncusol, a potent HCV inhibitor, targets HCV NS5A and is able to inhibit RNA replication of replicons harboring resistance mutations to anti-NS5A direct-acting antivirals. Dehydrojuncusol significantly inhibits HCV infection when added after virus inoculation of HCV genotype 2a (EC50=1.35 µM)[1]. |
| In Vitro | Dehydrojuncusol (Huh-7 cells were infected with HCV in cell culture; 0-9.4 μM; 48 hours) inhibits HCV infection in a dose-dependent manner. Dehydrojuncusol inhibits HCV infection in Primary human hepatocytes (PHH)[1]. The EC50 of dehydrojuncusol is 1.35 µM when added continuously, 8.21 µM when added during inoculation, and 1.53 µM when added postinoculation, confirming the major effect of the molecule at the postinoculation step. The toxicity of the compound on Huh-7 cells is also tested in parallel at different time points (24 h, 48 h, and 72 h). The results shows that the CC50 of Dehydrojuncusol Is approximately 75.6 µM, which is much higher than the active dose, yielding a selective index of 56[1]. Dehydrojuncusol is able to inhibit RNA replication of two frequent daclatasvir-resistant mutants (L31M or Y93H in NS5A). Dehydrojuncusol inhibits HCV RNA replication[1]. |
| Exact Mass | 264.11500 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 4.66400 |