Home
Products
Nothofagin
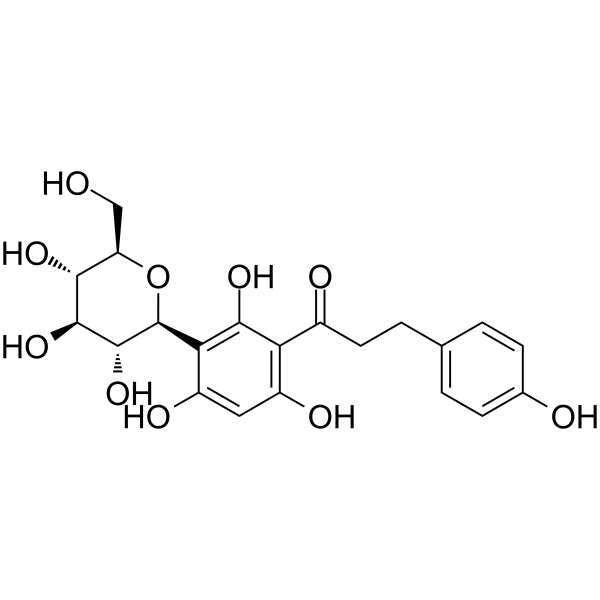


| Product Name | Nothofagin |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN05649 |
| CAS No.: | 11023-94-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C21H24O10 |
| Molecular Weight: | 436.4 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Chalcones |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The heartwoods of Nothofagus fusca |
| Solvent: | DMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc. |
| SMILES: | OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1O)O)O)c1c(O)cc(c(c1O)C(=O)CCc1ccc(cc1)O)O |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Nothofagin, a dihydrochalcone, is isolated from rooibos (Aspalathus linearis)[1]. Nothofagin downregulates NF-κB translocation through blocking calcium influx. Nothofagin has antioxidant activity and ameliorates various inflammatory responses such as the septic response and vascular inflammation[2]. |
| In Vitro | Nothofagin pre-treatment (0.1, 1, 10 μM) decreases the level of histamine release in RBL-2H3 and RPMCs cells. The production of cytokines are downregulated bynothofagin pre-treatment Nothofagin (TNF-α: 1-10 μM; IL-4: 0.1-10 μM, IL-6: 1-10 μM)[1]. Pre-treatment of DNPHSA-stimulated RBL-2H3 with Nothofagin (10 μM) markedly suppresses the phosphorylation of Lyn, Syk, and Akt[1]. Nothofagin (30 μM; for 6 hours) results in inhibited formation of LPS-induced (100 ng/mL; 4 hours) paracellular gaps with the formation of dense F-actin rings in HUVECs[2]. Nothofagin suppresses IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation both in vitro and in vivo[1]. |
| In Vivo | Nothofagin (1 mg/kg; orally; once a day; for 7 days) significantly increases the urinary volume of both normotensive (NTR) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR)[3]. Animal Model: Male Wistar normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats (3-4 months old) [3] Dosage: 1 mg/kg Administration: Orally; once a day; for 7 days Result: Significantly increased the urinary volume of both NTR and SHR. |
| Density | 1.594±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 711.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 249.4±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 436.136932 |
| LogP | 0.90 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.0 mmHg at 25°C |