Home
Products
Oenothein B


| Product Name | Oenothein B |
| Price: | Inquiry |
| Catalog No.: | CN03268 |
| CAS No.: | 104987-36-2 |
| Molecular Formula: | C68H48O44 |
| Molecular Weight: | 1569.1 g/mol |
| Purity: | >=98% |
| Type of Compound: | Phenols |
| Physical Desc.: | Powder |
| Source: | The herbs of Oenothera biennis |
| Solvent: | Chloroform, Dichloromethane, Ethyl Acetate, DMSO, Acetone, etc. |
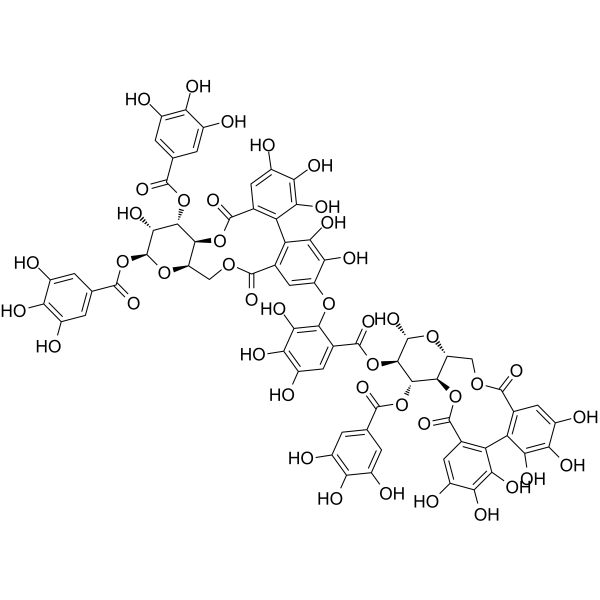
| SMILES: |
| Contact us | |
|---|---|
| First Name: | |
| Last Name: | |
| E-mail: | |
| Question: | |
| Description | Oenothein B is a dimeric macrocyclic ellagitannin and has widely pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, anti-HCV, and antitumor properties. Oenothein B is a potent and specific inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase[1][2]. |
| In Vitro | Oenothein B (15-45 µM; 12-72 hours) has a dose- and time-dependent inhibition rate effect on A549 cells in the range of 12 hours, 24 hours, 36 hours, 48 hours, 60 hours and 72 hours of exposure[1]. Oenothein B (15-45 µM; 24 hours) effectively inhibits the proliferation of A549 cells by inducing apoptosis and arresting cells at G1 stage[1]. Oenothein B (15-45 µM; 24 hours) not only increases the level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), but also induces the upregulation of intracellular apoptotic triggers (cleavage caspase-3, PARP, cytochrome c level in the cytosol, Bax)[1]. A549 cells[1]15 µM, 30 µM and 45 µM24 hoursArrested cells in the G1 phase.A549 cells[1]15 µM, 30 µM and 45 µM24 hoursBAX, p53, cytochrome c (cytoplasm) and PARP were unregulated significantly; Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 was decreased significantly in a concentration-dependent manner. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: A549 cells Concentration: 15 µM, 30 µM and 45 µM Incubation Time: 12 hours, 24 hours, 36 hours, 48 hours, 60 hours and 72 hours Result: Effectively inhibited the proliferation of A549 cells. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: A549 cells Concentration: 15 µM, 30 µM and 45 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Induced apoptosis in A549 cells. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: A549 cells Concentration: 15 µM, 30 µM and 45 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Arrested cells in the G1 phase. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: A549 cells Concentration: 15 µM, 30 µM and 45 µM Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: BAX, p53, cytochrome c (cytoplasm) and PARP were unregulated significantly; Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 was decreased significantly in a concentration-dependent manner. |
| In Vivo | Oenothein B (100-300 mg/kg; p.o.) has the ability to reduce neuroinflammation in the brain during systemic inflammation in ICR mice[3]. |
| Exact Mass | 1568.15000 |
| PSA | 732.84000 |
| LogP | 2.17020 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |